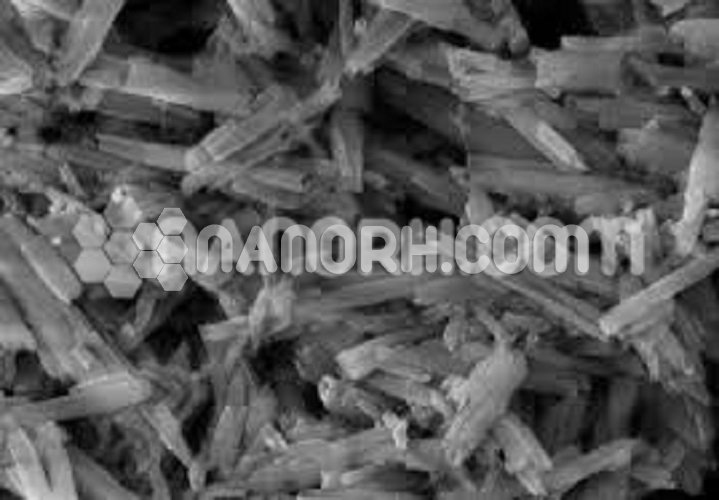
Titanium Metal Organic Framework
| Titanium Metal-Organic Framework | |
| Product No | NRE-17015 |
| CAS No. | 7440-32-6 |
| Formula | [Ti8O8(OH)4(C6H3C2O4NH2)6] |
| APS | <40µm (can be customized) |
| Molecular Weight | 604.87 g/ mol |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Density | 0.35 g/ cm3 |
| Pore Size | ~10Å |
| Odor | Odorless |
| SSA | ~1300 m2/g (BET) |
| Color | Light green |
Titanium Metal-Organic Framework
Introduction
Titanium Metal-Organic Frameworks (Ti-MOFs) are a type of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) that incorporate titanium (Ti) ions as the central metal component. These materials consist of titanium ions coordinated with organic ligands, which form highly porous, crystalline structures. Ti-MOFs have gained attention in recent years due to their remarkable properties, such as high chemical stability, tunable porosity, and photocatalytic activity. Due to these characteristics, Ti-MOFs find applications across various fields, including catalysis, energy storage, gas separation, environmental remediation, and biomedical applications.
Applications
Catalysis Ti-MOFs are widely studied for their catalytic properties. The titanium centers in these materials can act as Lewis acid catalysts, which can facilitate a variety of chemical reactions. These include oxidation reactions, such as epoxidation of alkenes, oxidative coupling, and C-H activation reactions.
Photocatalysis One of the most promising applications of Ti-MOFs is in photocatalysis. Titanium is known for its photocatalytic properties, particularly under ultraviolet (UV) light. Ti-MOFs have been studied for solar energy conversion processes, such as photocatalytic water splitting for hydrogen production and the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into useful chemicals. The photocatalytic activity of Ti-MOFs can help drive environmentally friendly reactions, such as degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater, utilizing solar energy to break down toxic substances. Ti-MOFs are thus a key material in the development of renewable energy technologies and environmental remediation.
Gas Storage and Separation Ti-MOFs are also well-suited for gas storage and separation due to their large surface area and tunable porosity. These materials can efficiently adsorb and store gases such as hydrogen (H₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄). This makes Ti-MOFs useful for applications in hydrogen storage, carbon capture, and natural gas storage. Ti-MOFs can selectively adsorb specific gases, based on size and chemical interactions, which makes them ideal for gas separation. For example, Ti-MOFs can separate CO₂ from other gases in industrial emissions, aiding in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to environmental sustainability.