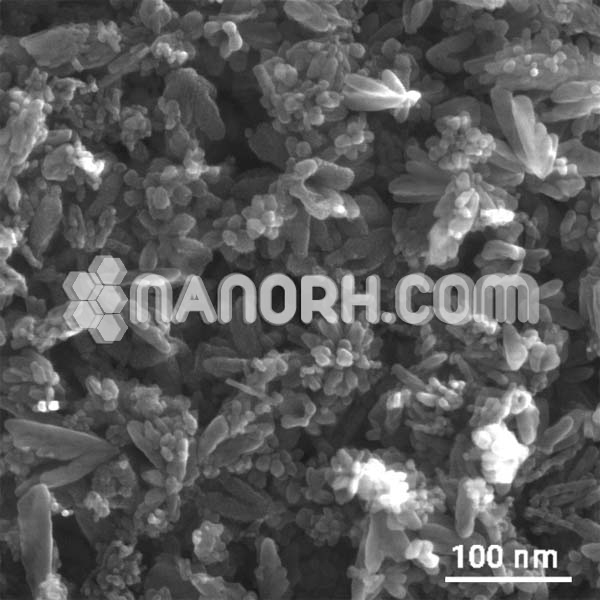
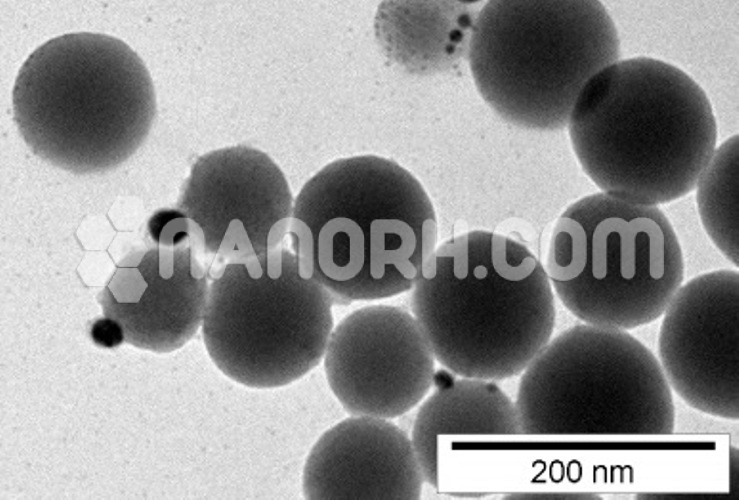
Dysprosium Metal Organic Framework (Dy-MOF, Purity: 99%, APS:30-40µm)
| Dysprosium Metal-Organic Framework | |
| Product No | NRE-17005 |
| CAS No. | 7429-91-6 |
| Formula | Dy(pyda)3Ca1.5(H2O)6} ⋅ 5.5H2O (1) |
| APS | <40µm (can be customized) |
| Molecular Weight | 158.925 g/mol |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Density | 0.35 g/ cm3 |
| Pore Size | ~10Å |
| Form | Powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| SSA | ~1300 m2/g (BET) |
| Color | Greenish-yellow |
Dysprosium Metal-Organic Framework
Applications
Magnetic and Spintronic Applications Dysprosium is known for its strong magnetic properties, particularly its high magnetic anisotropy. Dy-MOFs can be used in the development of advanced magnetic materials, particularly in applications like data storage, magnetic sensors, and quantum computing. Their ability to control and manipulate spin states makes them promising candidates for use in spintronics, a field that relies on the electron’s spin rather than its charge to store and process information.
Gas Storage and Separation The high porosity and surface area of Dy-MOFs make them ideal candidates for storing and separating gases. Like other MOFs, Dy-MOFs can adsorb gases such as hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide. In particular, their ability to selectively adsorb certain gases could make them valuable in applications like natural gas storage, carbon capture, and air purification. The magnetic properties of Dy-MOFs may also play a role in enhancing gas adsorption through interactions with certain gases.
Catalysis Dy-MOFs exhibit potential in catalysis, especially for reactions that benefit from the unique electronic properties of dysprosium. The metal centers in Dy-MOFs can serve as active sites for catalyzing chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and other organic transformations. These materials may be especially useful in heterogeneous catalysis, where they can enable reactions without the need for soluble catalysts, improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Sensing and Detection The luminescent properties of dysprosium, combined with the porous nature of Dy-MOFs, allow these materials to be used in sensing applications. Dy-MOFs can be designed to selectively absorb certain molecules, such as gases or pollutants, and emit detectable light when they interact with the target species. This makes Dy-MOFs suitable for chemical and environmental sensing applications, including the detection of toxic gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and heavy metals.
Energy Storage Dy-MOFs are being explored for their potential use in energy storage systems, such as batteries and supercapacitors. The high surface area and tunable structure of these materials enable them to store and release energy efficiently. Additionally, their magnetic properties might also be leveraged to develop advanced materials for energy storage and conversion, potentially improving the capacity and performance of energy storage devices.
Luminescent and Optical Applications The strong fluorescence of dysprosium ions makes Dy-MOFs ideal candidates for optical applications. These materials can be used in luminescent sensors, light-emitting devices, and optical imaging.