| Barium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5020 |
| CAS No. | 7787-32-8 |
| Formula | BaF2 |
| APS | <50nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 175.34 g/mol |
| Density | 4.893 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1368 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2260 °C |
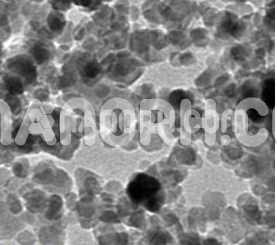
Barium Fluoride Nanopowder
Barium Fluoride nanopowder is an inorganic compound composed of barium and fluorine. In its bulk form, barium fluoride is a white crystalline solid, but when reduced to nanopowder form, its properties undergo significant enhancement. The nanopowder consists of particles typically sized between 1 to 100 nanometers, offering a large surface area relative to its volume. This results in superior reactivity, better dispersion, and novel optical, chemical, and physical properties compared to the bulk material.
Barium fluoride is well-known for its exceptional optical transparency in the infrared (IR) region, making it highly valuable in optical technologies. When reduced to nanopowder form, these optical properties are improved, and the material becomes more effective for various advanced applications, such as in infrared optics, catalysis, electronic devices, and medical imaging.
Nanotechnology allows for the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, where unique behaviors emerge, making barium fluoride nanoparticles a highly sought-after material in both research and industrial applications. Due to its versatile properties, barium fluoride nanopowder has significant potential in a wide range of fields, from optics and electronics to environmental and medical uses.
Properties
High Surface Area: The nanopowder form of barium fluoride possesses an increased surface area compared to its bulk counterpart, which leads to greater reactivity. This property makes it an excellent candidate for use in catalytic applications, adsorption processes, and in the synthesis of nanocomposites.
Optical Transparency: Barium fluoride is renowned for its high transmittance in the infrared region, making it an ideal material for optical devices like infrared lenses, windows, and filters. The nanopowder form enhances these properties and improves the optical performance in laser systems and other precision optical instruments.
Electrical and Ionic Conductivity: Due to the nanometer-scale particle size, nanopowder can exhibit increased ionic conductivity, which is beneficial for electrochemical devices such as supercapacitors and batteries.