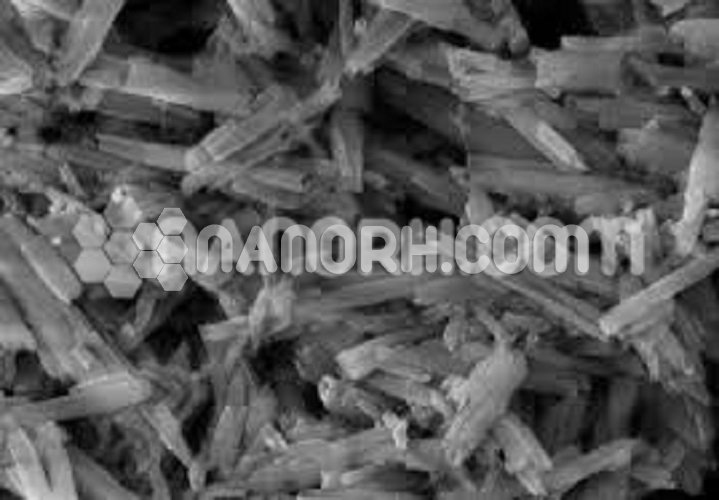
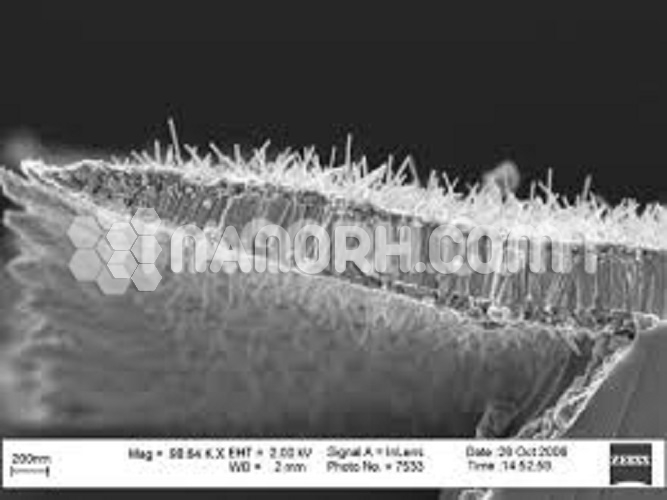
Tungsten(VI) Oxide Nanowires
Tungsten(VI) Oxide Nanowires are nanoscale wires with various applications including optical coatings, electronics, liquid crystals, transparent thin films and medical therapies. Silver nanowires are generally immediately available in most volumes.
| Tungsten(VI) Oxide Nanowires | |
| Product No | NRE-13014 |
| CAS No. | 1314-35-8 |
| Formula | WO3 |
| Average diameter | 150-200nm |
| Average Length | up to 15um |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Weight | 231.84 g/mol |
| Density | 7.16 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1473 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1700 °C |
Tungsten(VI) Oxide Nanowires are nanoscale wires with various applications including optical coatings, electronics, liquid crystals, transparent thin films, and medical therapies. Silver nanowires are generally immediately available in most volumes. Elements produce too many standard grades when applicable, including Mil Spec, ACS, Reagent and Technical Grade; Food, Agricultural, and Pharmaceutical Grade.
Applications of Tungsten(VI) Oxide Nanowires (WO₃ Nanowires)
Photocatalysis and Environmental Remediation:
Pollutant Degradation: WO₃ nanowires are excellent photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants, such as dyes, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals, under UV or visible light. This makes them valuable in water treatment and air purification.
Photocatalytic Water Splitting: WO₃ nanowires can facilitate water splitting to produce hydrogen (H₂) when illuminated, making them promising materials for sustainable hydrogen production and solar energy conversion.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Supercapacitors: Due to their high surface area and excellent electrochemical performance, WO₃ nanowires can be used as electrode materials in supercapacitors, offering high energy density, fast charge/discharge rates, and long cycling stability.
Batteries: WO₃ nanowires are also being explored for use in lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. Their ability to intercalate lithium or sodium ions makes them effective anode materials that can enhance battery capacity, efficiency, and cycle life.
Photovoltaic Devices: WO₃ nanowires can be incorporated into solar cells, particularly in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) and perovskite solar cells, where they help improve light absorption and electron transport, thereby increasing the efficiency of energy conversion.
Electrochromic Devices and Smart Windows:
Smart Windows: WO₃ nanowires are used in electrochromic devices that can change their optical properties (such as transparency or color) in response to an applied voltage. These materials are used in smart windows, which can regulate the amount of light and heat entering a building, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
Displays: The ability of WO₃ to change color with the application of voltage makes it suitable for use in electrochromic displays and smart mirrors, where dynamic control of optical properties is desired.
Gas Sensing:
NO₂ and CO Detection: WO₃ nanowires are used in gas sensors for detecting gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). Their high surface area and the ability to interact with these gases make WO₃ nanowires highly sensitive and selective for gas detection, which is valuable in environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications.
Humidity Sensors: WO₃ nanowires have been shown to exhibit humidity-sensing properties, as their conductivity changes with varying moisture levels. This makes them useful for humidity sensors in applications such as weather stations and climate control systems.