Lead Nanowires
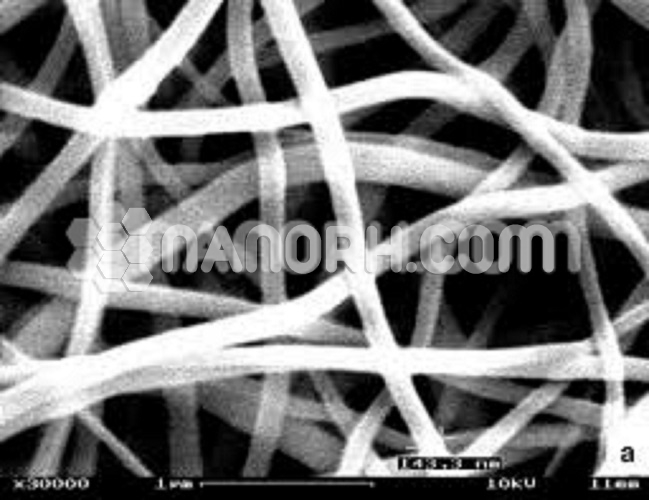
Lead Nanowires are elongated nanostructures with an average diameter of 80±20 nm and length of up to several millimeters. Applications for lead nanowires include optical devices, sensors, solar cells, and microelectronics. Lead nanowires are generally immediately available in most volumes, including bulk orders. Nano Research Elements produces to many standard grades when applicable, including Mil Spec ,ACS, Reagent and Technical Grade; Food, Agricultural and Pharmaceutical Grade
| Lead Nanowires | |
| Product No | NRE-13005 |
| CAS No. | 7439-92-1 |
| Formula | Pb |
| Average diameter | 30-50nm |
| Average Length | up to 500nm |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Weight | 207.2 g/mol |
| Density | 11.35 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 327.5 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1749 °C |
Lead Nanowires are elongated nanostructures with an average diameter of 80±20 nm and length of up to several millimeters. Applications for Pb nanowires include optical devices, sensors, solar cells, and microelectronics.
Applications of Lead Nanowires
Nanoelectronics:
Interconnects and Conductive Pathways: Due to their high conductivity, lead nanowires are considered potential candidates for use in nanoscale interconnects in integrated circuits (ICs) and nanoelectronic devices. Their small size and ability to efficiently carry electrical signals at the nanoscale make them valuable for next-generation electronic devices where traditional materials may no longer meet performance requirements.
Resistive Switching Devices: Lead nanowires can be used in resistive switching memory devices, such as memristors, where their resistance can be altered by the application of a voltage. These devices are a promising alternative to conventional flash memory for data storage.
Sensors and Biosensors:
Chemical and Gas Sensors: Lead nanowires are studied for use in chemical and gas sensing applications, where their high surface area allows for significant interactions with gases or chemicals. They can be functionalized to detect specific gases such as NO₂, NH₃, or CO. Changes in the electrical resistance or capacitance of the nanowires upon exposure to certain chemicals can be measured and used to detect the presence of target substances.
Biosensors: Lead nanowires can be employed as the sensing element in biosensors for detecting biomolecules such as DNA, proteins, and antibodies. The high surface-area-to-volume ratio and the ability to modify the nanowires’ surface with functional groups make them suitable for use in medical diagnostics, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring.
Catalysis:
Electrocatalysis: Lead nanowires, due to their conductive properties, are explored for use in electrocatalysis applications, such as in fuel cells or water splitting for hydrogen production. The ability to manipulate the electronic structure of allows for fine-tuning of their catalytic activity, making them useful in energy conversion technologies.
Chemical Catalysis: Lead is also a known catalyst for some organic reactions, including oxidation reactions and hydrogenation reactions. Lead nanowires may serve as effective catalytic supports in heterogeneous catalysis due to their increased surface area and reactivity at the nanoscale.