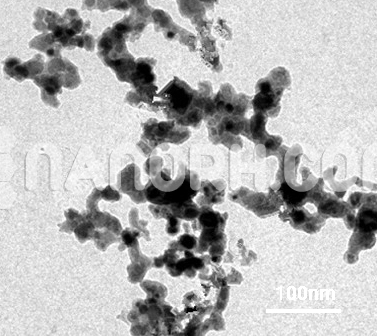
Silver Nanotubes
Silver Nanotubes (Single-Walled) are tubular ultra high surface area nanostructures. Nanoscale Silver Nanotubes are typically 10 – 100 nanometers (nm) with specific surface area (SSA) in the 10 – 75 m2/g range. Silver Nanotubes are also available in coated and dispersed forms. They are also available as a dispersion through the AE Nanofluid production group.
| Silver Nanotubes | |
| Product No | NRE-14018 |
| CAS No. | 7440-22-4 |
| Formula | Ag |
| Average diameter | 30-50nm |
| Average Length | up to 200µm |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Weight | 107.87 g/mol |
| Density | 10490 kg/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 961.78 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2162 °C |
Silver Nanotubes (Single-Walled) are tubular ultra-high surface area nanostructures. Nanoscale Silver Nanotubes are typically 10 – 100 nanometers (nm) with specific surface area (SSA) in the 10 – 75 m2/g range. Ag Nanotubes are also available in coated and dispersed forms. They are also available as a dispersion through the AE Nanofluid production group. Nanofluids are generally defined as suspended nanoparticles in solution either using surfactant or surface charge technology. Nanofluid dispersion and coating selection technical guidance is also available. Other nanostructures include nanorods, nanowhiskers, nanohorns, nanopyramids, and other nanocomposites. Surface functionalized nanoparticles allow for the particles to be preferentially adsorbed at the surface interface using chemically bound polymers.
Applications:
Electronics and Conductive Materials:
Flexible Electronics: Due to their high conductivity and mechanical strength, SWNTs are being explored in the development of flexible electronic devices such as touchscreens, sensors, and wearable electronics.
Conductive Ink: SWNTs can be used in printed electronics, where they are incorporated into conductive inks for the fabrication of printed circuits or antennas.
Transparent Conductors: They can serve as transparent conductive films in devices like solar cells, touchscreens, and OLED displays, providing a transparent alternative to traditional metal-based conductors.
Sensors and Detection Devices:
Gas Sensors: Silver nanotubes are highly sensitive to changes in their environment, making them suitable for gas sensing. For instance, they can detect trace amounts of gases like ammonia, nitrogen dioxide, or carbon monoxide due to their high surface area and reactivity.
Biosensors: SWNTs can be functionalized with biomolecules for use in biosensors, detecting specific biological markers in medical diagnostics or environmental monitoring.
Catalysis:
Catalytic Processes: Silver is known to be an effective catalyst in certain chemical reactions, such as those involving oxidation or reduction. Silver nanotubes, due to their large surface area, can be used as catalysts in chemical processes, providing enhanced reactivity compared to bulk silver.
Fuel Cells: In particular, silver nanotubes could play a role in improving the efficiency of fuel cells by acting as catalysts in the conversion of hydrogen or other fuels to electricity.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Batteries and Supercapacitors: The high surface area of SWNTs allows them to be used in energy storage devices such as supercapacitors or batteries, enhancing their energy density and charging speed.
Medical Applications:
Drug Delivery: The high surface area and ability to functionalize silver nanotubes make them promising candidates for use in targeted drug delivery systems, where they can carry pharmaceutical agents to specific cells or tissues in the body.
Antimicrobial Properties: Silver has well-known antimicrobial properties, and these can be enhanced when silver is in the form of nanotubes. SWNTs are being studied for use in coatings or materials that prevent bacterial growth, potentially useful in medical devices, wound dressings, or water purification.