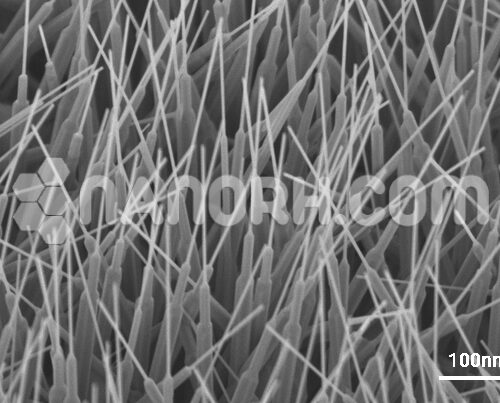
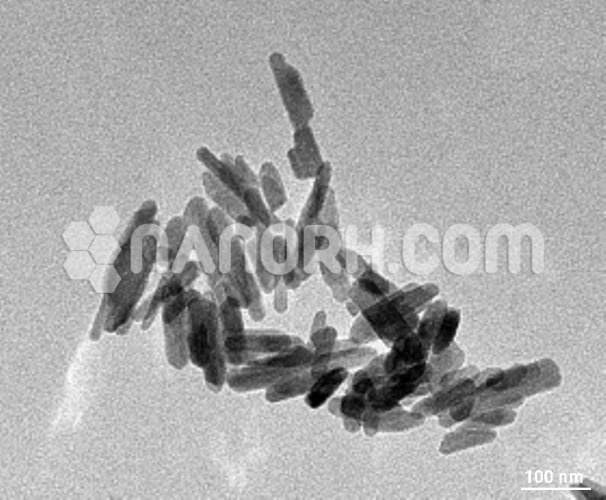
Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Ethanol Dispersion (3-10nm, 5wt% in Ethanol)
High precision polishing-for the computer disk heads, the panels, and chips, optics lenses and jewelery; Additives in Polymer complexes-can be used as a additives in rubber, glass, ceramic, and textile fabric material; Erosion-resistant diamond films/coatings; Biomedical materials (artificial bones and joints);
| Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Ethanol Dispersion | |
| Product No | NRE-22039 |
| CAS No. | 7782-40-3 |
| Formula | C |
| Molecular Weight | 12.01 g/mol |
| APS | <10 nm (can be customized) |
| Purity | > 98.3% |
| Color | Grey |
| Density | 3.51 gm/cm3 |
| Solvent | Ethanol (as per requirement) |
| pH | NA |
Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Ethanol Dispersion
High precision polishing-for the computer disk heads, the panels, and chips, optics jewelry; Additives in Polymer complexes-can be used as an additive in rubber, glass, ceramic, and textile fabric material; Erosion-resistant diamond films/coatings; Biomedical materials (artificial bones and joints); Biosensors; Chemical Sensors; Field electron emission materials; Heat-resistant diamond films/coatings; Integrated circuit substrates; Photoelectric sensors; Self-lubricating, wear-resistant composite coating; Pressure-limiting sensors; Radiation-resistant diamond films/coatings; Reinforcing agents for rubber, plastics, and resin; Seed crystal for growing larger diamond; High-strength abrasive material.
Applications
Diamond nanoparticles dispersed in ethanol offer a wide range of applications across multiple industries due to their unique combination of properties. Here are some of the key applications:
Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery Systems: Due to their biocompatibility and small size, diamond nanoparticles can be used as drug carriers in targeted delivery systems. When dispersed in ethanol, nanodiamonds can be loaded with pharmaceutical drugs and directed to specific sites in the body, such as tumor cells or infected tissues. Their surface can be functionalized to improve drug loading efficiency and release control.
Bioimaging and Diagnostics: Nanodiamonds can be used as contrast agents in imaging techniques like fluorescence microscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Their small size and high surface area allow them to carry imaging agents, while their biocompatibility ensures safe interaction with biological systems. The dispersion in ethanol ensures that the particles are uniformly distributed, improving the consistency of the imaging process.
Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: Nanodiamonds have shown promise in promoting wound healing due to their anti-inflammatory properties. When suspended in ethanol, these nanoparticles can be applied topically in creams or ointments to accelerate healing and tissue regeneration by promoting cell growth and repair.
Electronics and Nanocomposites
Thermal Management: Due to their excellent thermal conductivity, diamond nanoparticles are used in thermal interface materials (TIMs) and nanocomposites to improve heat dissipation in electronic devices like semiconductors, LEDs, and microprocessors. Dispersion in ethanol allows for uniform distribution of the nanoparticles in polymer matrices, resulting in improved thermal performance in electronics.
Conductive Materials: When integrated into conductive inks, diamond nanoparticles dispersed in ethanol can be used in printed electronics. These inks can be applied to various substrates to create flexible, high-performance electronic devices, including wearable sensors, flexible displays, and solar cells.
Nanocomposites for Wearables: Diamond nanoparticles are used to enhance the mechanical properties of nanocomposites, such as increasing the strength, durability, and conductivity of materials used in wearable electronics. Ethanol dispersion helps maintain the uniformity of the nanoparticles in the composite material.
Catalysis and Environmental Applications
Catalytic Reactions: Diamond nanoparticles can serve as catalysts or catalyst supports in chemical reactions due to their high surface area and stability. When dispersed in ethanol, nanodiamonds can be used to facilitate reactions such as hydrogenation, oxidation, and polymerization. Their unique properties also make them effective in reducing unwanted by-products and improving reaction efficiency.
Pollution Control: Nanodiamonds dispersed in ethanol are also used in environmental cleanup applications. Due to their high surface reactivity, they can adsorb pollutants such as heavy metals, toxins, and organic compounds from water or air. These particles can help purify water sources and reduce environmental pollution.
Sensors for Environmental Monitoring: Nanodiamonds can be used in environmental sensors to detect gases, toxins, and pollutants. Their high surface area allows them to interact with target molecules, producing measurable signals for detection. Ethanol dispersion is often used to prepare these nanoparticles for sensor integration.
Abrasive and Wear-resistant Coatings
Lubricants and Coatings: Diamond nanoparticles, due to their hardness and wear resistance, are used in the formulation of advanced lubricants and wear-resistant coatings. These coatings are ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. The ethanol dispersion of diamond nanoparticles ensures that the particles are well-dispersed within the lubricant, providing consistent performance.
Cutting and Grinding Tools: Due to their hardness, diamond nanoparticles are also used in cutting, grinding, and polishing tools. When dispersed in ethanol, nanodiamonds are mixed with other abrasive materials to improve the efficiency and precision of these tools, making them ideal for fine machining and surface finishing.