| Zinc Iron Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-4021 |
| CAS No. | 12063-19-3 |
| Formula | ZnFe2O4 |
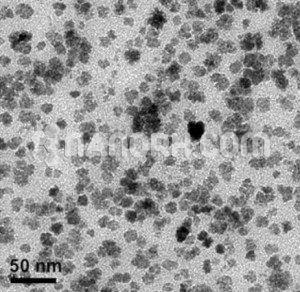
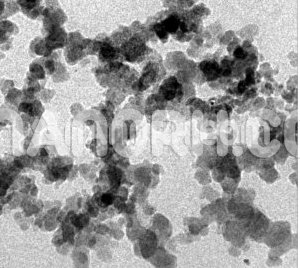
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Brown |
| Molecular Weight | 241.08 g/mol |
| Density | 5.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
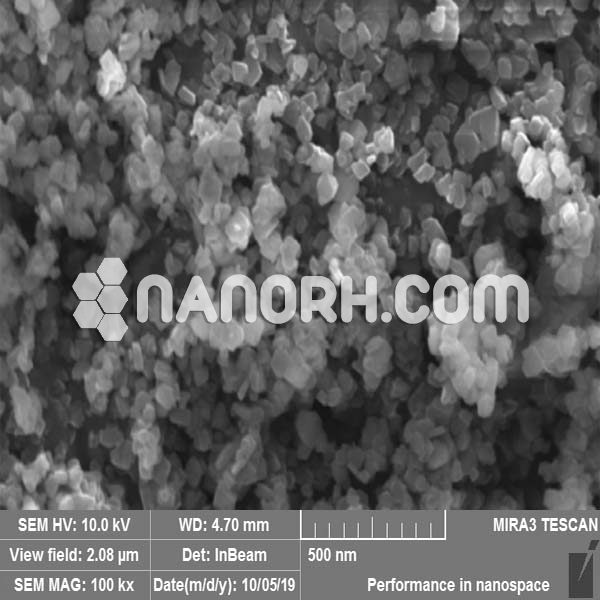
Zinc Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Zinc iron oxide nanoparticles are a class of multifunctional nanoparticles with unique physical and chemical properties due to their composition and nanoscale dimensions. These nanoparticles consist of zinc oxide (ZnO) and iron oxide (Fe₂O₃) in a spinel structure, often referred to as zinc ferrite, which offers both ferromagnetic and semiconductor properties.
Applications
Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery: The magnetic properties of ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles allow for targeted drug delivery, especially under the influence of an external magnetic field. This makes them ideal candidates for controlled drug release systems.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles can serve as contrast agents in MRI, enhancing the resolution of images due to their superparamagnetic properties.
Cancer Treatment: Their magnetic characteristics can also be leveraged in hyperthermia-based cancer treatments. When exposed to an alternating magnetic field, these nanoparticles can generate localized heat, killing cancer cells.
Biosensing: ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles are utilized in biosensors for detecting various biological molecules or pathogens due to their high surface area and tunable properties.
Environmental Remediation:
Water Purification: ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles can be employed to remove heavy metals (such as arsenic or lead) and organic pollutants from water, making them highly useful in water treatment and purification technologies.
Pollutant Degradation: Their photocatalytic properties enable them to degrade organic pollutants, such as dyes and pesticides, under UV or visible light, aiding in environmental cleanup.
Air Purification: ZnFe₂O₄-based materials can be used in air filtration systems to remove toxic gases, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Catalysis:
Catalysis in Chemical Reactions: ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles are often used as catalysts or catalyst supports in various organic reactions, such as the degradation of pollutants, synthesis of biodiesel, and the production of hydrogen from water splitting.
Electrocatalysis: ZnFe₂O₄ can act as an efficient electrocatalyst in applications like water splitting (hydrogen production), fuel cells, and lithium-ion batteries due to their high electronic conductivity and catalytic properties.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Batteries: ZnFe₂O₄ nanoparticles are being explored as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries. They can offer high capacity and stability during cycling.
Supercapacitors: These nanoparticles are also used in supercapacitors, where they provide high energy and power density for rapid charging and discharging cycles.
Photovoltaic Devices: ZnFe₂O₄ can be used as a photoelectrode material in solar cells, due to its semiconductor properties and light absorption capabilities.