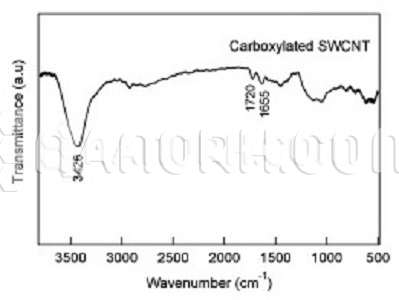
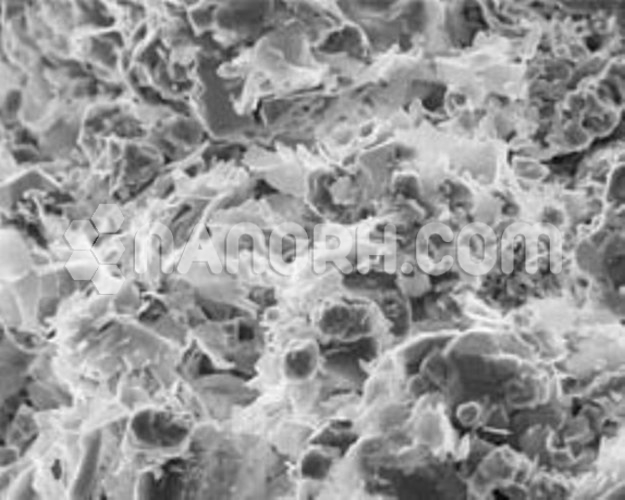
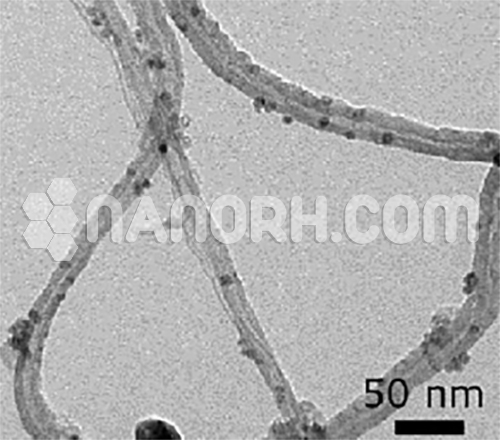
Carbon Nanotube-TiO2 Prepared by Electrostatic Adsorption (CNTs 20wt% : TiO2-rutile 80wt%)
CNTs (Outside diameter: >50nm, Inside diameter: 5-15nm, length: 5-20um)–treated by Cationic surfactant (Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide); TiO2 (Rutile, 100nm~300nm, spherical)–TiO2 rutile crystal between adjacent Octahedrons, oxygen from oxygen a key Connected to the horizontal edge direction exists the larger density of oxygen with negative electrical. By electrostatic interactions, TiO2 rutile and CNTs through Electrostatic adsorption self-assembly form a uniform and stable complex. Titanium dioxide particles effectively isolate the agglomerates of CNTs and form stable CNTs/TiO2 composite. Titanium dioxide has a large surface area with electronegativity, therefore the nanopowder TiO2 rutile can adsorb more of CNTs…..
| Carbon Nanotube-TiO2 Prepared by Electrostatic Adsorption | |
| Product No | NRE-1227 |
| CAS No. | 7440-44-0/13463-67-7 |
| Formula | CNTs-TiO2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 91.8765 g/mol |
| Density | 4.23 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Carbon Nanotube-TiO2 :-
Carbon Nanotube-TiO2 (Outside diameter: >50nm, Inside diameter: 5-15nm, length: 5-20um)–treated by Cationic surfactant (Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide); TiO2 (Rutile, 100nm~300nm, spherical)–TiO2 rutile crystal between adjacent Octahedrons, oxygen from oxygen a key Connected to the horizontal edge direction exists the larger density of oxygen with negative electrical. By electrostatic interactions, TiO2 rutile and CNTs through Electrostatic adsorption self-assembly form a uniform and stable complex. Titanium dioxide particles effectively isolate the agglomerates of CNTs and form stable CNTs/TiO2 composite. Titanium dioxide has a large surface area with electronegativity, therefore the nanopowder TiO2 rutile can adsorb more of CNTs.
Applications
Photocatalysis for Environmental Remediation
Water Treatment: One of the most significant applications of CNT-TiO₂ composites is in water purification. TiO₂ is an effective photocatalyst under UV light, capable of degrading harmful organic pollutants (such as dyes, pesticides, and industrial waste) in water. CNTs improve the photocatalytic efficiency by increasing electron transfer, which prevents recombination of electron-hole pairs and enhances pollutant degradation.
Air Purification: CNT-TiO₂ composites are also used for air purification. TiO₂’s photocatalytic ability can break down volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants when exposed to UV light. CNTs help by increasing the material’s stability and improving the charge separation efficiency during the photocatalytic process.
Degradation of Organic Pollutants: CNT-TiO₂ composites are highly effective at degrading organic pollutants in wastewater, especially under sunlight or UV light, which is an environmentally friendly way to treat contaminants. These composites can break down hazardous organic compounds into harmless by-products like CO₂ and H₂O.
Energy Production and Storage
Solar Cells: CNT-TiO₂ composites are being investigated for use in solar cells, particularly in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The CNTs can improve the conductivity of TiO₂-based electrodes, increasing the overall efficiency of energy conversion by reducing charge recombination and enhancing electron transport.
Hydrogen Production: The photocatalytic properties of TiO₂ can also be used in hydrogen production via water splitting. CNTs enhance the efficiency of the process by improving the electron transport properties and preventing charge recombination, which increases the overall efficiency of hydrogen generation from water under light irradiation.
Supercapacitors: The high electrical conductivity and large surface area of CNT-TiO₂ composites make them promising materials for supercapacitors. The material can store and release large amounts of energy, making it suitable for use in energy storage devices and electric vehicles. The composite can improve charge/discharge rates, capacity, and cycling stability.