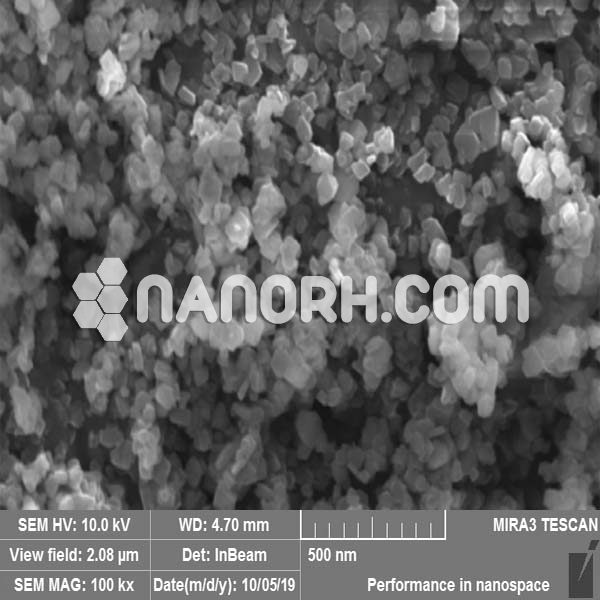
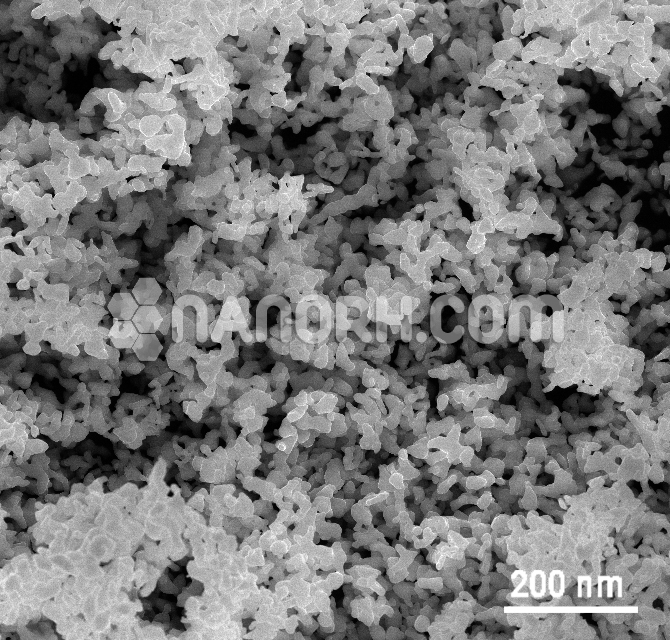
| Zirconium(II) Hydride Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-5269 |
| CAS No. | 7704-99-6 |
| Formula | ZrH2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 93.23988 g/mol |
| Density | 5.56 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Zirconium(II) Hydride Powder
Introduction
Zirconium(II) hydride (ZrH₂) is an inorganic compound that forms when zirconium metal reacts with hydrogen. It exists as a powder or in bulk form and has distinct properties that make it useful in a variety of industrial, nuclear, and technological applications. The zirconium in ZrH₂ has a +2 oxidation state, and the compound is generally synthesized by reacting zirconium metal with hydrogen gas at elevated temperatures and pressures. This hydride is a metal hydride with excellent thermal and mechanical properties, especially when used in high-temperature and high-energy environments.
Zirconium hydride is notable for its ability to absorb and release hydrogen, making it useful in hydrogen storage and fuel cell applications. Additionally, its unique properties, such as high thermal conductivity, neutron absorption capability, and corrosion resistance, contribute to its versatility in different technological fields.
Properties of Zirconium(II) Hydride Powder
Hydrogen Storage Capacity:
ZrH₂ is known for its ability to absorb and store hydrogen gas, making it an effective material for hydrogen storage systems. This property is significant in the development of hydrogen-based energy systems, such as fuel cells.
Neutron Absorption:
Zirconium hydride has excellent neutron-absorbing properties, which make it an ideal material for use in nuclear reactors. It is commonly used as a neutron moderator in nuclear reactors to slow down neutrons and enable more efficient nuclear reactions.
Thermal Conductivity:
ZrH₂ has good thermal conductivity, which makes it useful in systems that require efficient heat dissipation, especially in high-temperature applications.
Corrosion Resistance:
Like other forms of zirconium, ZrH₂ exhibits high resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments such as high-temperature or acidic conditions.
Mechanical Strength:
Zirconium hydride has adequate mechanical strength, which contributes to its utility in demanding environments where both high temperature and structural integrity are required.
Thermal Expansion:
ZrH₂ has a relatively low thermal expansion coefficient, making it useful in applications where dimensional stability is required under thermal cycling.