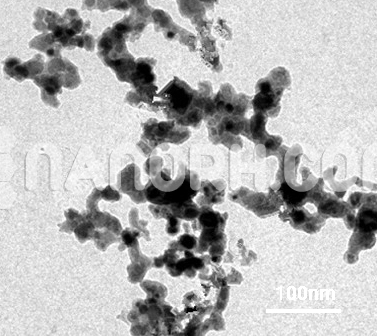
Cu(OH)2 Nanowire / Copper(II) Hydroxide Nanowire (Cu(OH)2, 99.5%, Diameter 50nm, Length 3-5um)
Copper(II) hydroxide is also occasionally used as ceramic colorant. Copper(II) hydroxide has been combined with latex paint, making a product designed to control root growth in potted plants. Secondary and lateral roots thrive and expand, resulting in a dense and healthy root system and many other fields
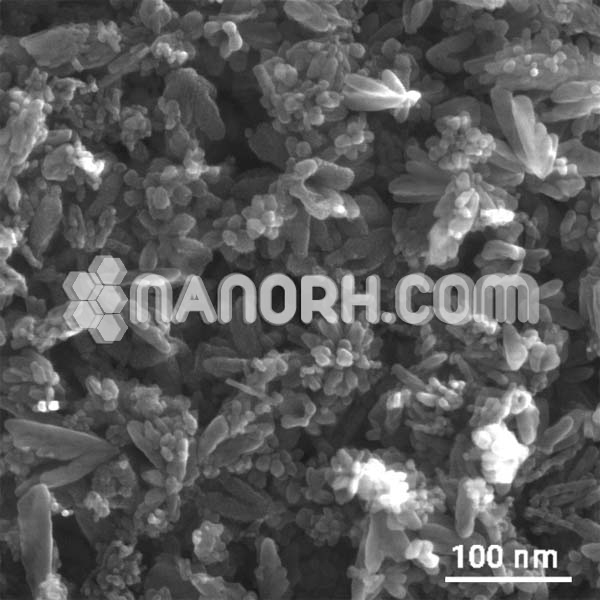
| Copper(II) Hydroxide Nanowire | |
| Product No | NRE-13002 |
| CAS No. | 20427-59-2 |
| Formula | Cu(OH)2 |
| Average diameter | 30-50nm |
| Average Length | up to 500nm |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Weight | 97.56068 g/mol |
| Density | 3.37 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 80° C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Copper(II) Hydroxide Nanowire :- It has been used as an alternative to the Bordeaux mixture, a fungicide, and nematicide. Copper(II) hydroxide is also occasionally used as a ceramic colorant. Copper(II) hydroxide has been combined with latex paint, making a product designed to control root growth in potted plants. Secondary and lateral roots thrive and expand, resulting in a dense and healthy root system and many other fields–The product is nano grade size. It is more active and more effective in application with a large surface area about 13.98 m2/g– the product is for research purpose.
Applications
charge/discharge cycles.
Battery Electrodes: Copper(II) hydroxide nanowires can be used as electrodes in batteries, particularly in lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. The nanowires enhance the electrochemical performance, including specific capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability.
Sensors:
Gas Sensors: Cu(OH)₂ nanowires are used in gas sensors to detect gases such as ammonia (NH₃), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂). Their high surface area allows for efficient adsorption of gas molecules, and their electrical properties can be tuned for sensitive and selective detection.
Biosensors: Copper(II) hydroxide nanowires can be employed in biosensors for detecting biomolecules. The ability to functionalize their surface allows for selective detection of specific biomarkers or pathogens, making them suitable for medical diagnostics or environmental monitoring.
Water Treatment:
Water Purification: Due to their ability to adsorb heavy metals and organic contaminants, Cu(OH)₂ nanowires are used in water treatment applications. They can remove toxic ions such as lead (Pb²⁺) and mercury (Hg²⁺) from water through adsorption, providing an effective means of water purification.
Desalination: Research has shown that copper(II) hydroxide nanowires can be part of desalination systems that help remove salts from seawater, improving the efficiency of desalination processes for producing potable water.