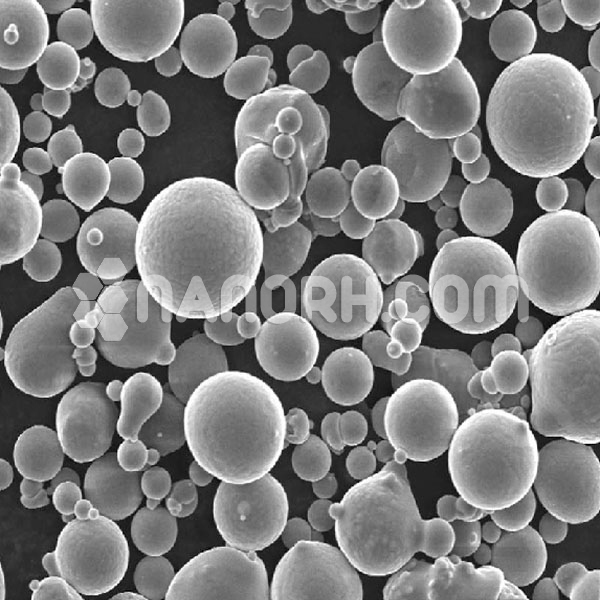
| Atomized spherical Aluminum based alloy powder | |
| Product No | NRE-60100 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Mesh | 30-500 mesh |
| Color | Silver Gray |
AlZn8020
|
Composition |
wt. (%) | |||||||
| Zn | Fe | Si | Cu | Ti | Mg | Mn | Al | |
| 19.055% | 0.095% | 0.033% | 0.01% | 0.005% | 0.01% | 0.02% | balance | |
AlZn9010
|
Composition |
wt. (%) | |||||||
| Zn | Fe | Si | Cu | Ti | Mg | Mn | Al | |
| 0.095% | 0.095% | 0.033% | 0.01% | 0.005% | 0.01% | 0.02% | balance | |
Theoretical density and combustion heat
| Sample
(g/cm³) |
Theoretical density
(g/cm³) |
Combustion Heatk
(J/g) |
Calculated value according to alloy ratio (J/g) |
| Al-Zn9010-6μm | 2.87 | 26.61 | 26.76 |
| Al-Zn8020-6μm | 3.08 | 23.42 | 24.38 |
Atomized spherical Aluminum based alloy powder
Applications of Atomized Spherical Aluminum-Based Alloy Powders:
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
Process: Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
Applications:
Production of lightweight, complex parts with minimal material waste.
Aerospace (engine components, brackets, heat exchangers), automotive (engine blocks, lightweight chassis), medical (implants, prosthetics).
Features: The powders’ excellent flowability and consistent particle size make them ideal for high-precision 3D printing.
Powder Metallurgy (PM):
Process: Sintering
Applications:
Gears, bearings, automotive components (brackets, structural parts).
Advantages: Atomized spherical powders enable better densification, improved mechanical properties, and reduced porosity in final parts.
Thermal Spray Coatings:
Process: Plasma spraying, flame spraying, HVOF (High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel)
Applications:
Protective coatings on parts exposed to high temperatures and wear, such as turbine blades, heat exchangers, and marine components.
Features: Aluminum-based coatings offer corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and thermal protection.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM):
Process: Powder mixed with binder, then injected into molds and sintered.
Applications:
Complex, small parts like connectors, brackets, and internal components.
Advantages: Ideal for producing high-density parts with intricate designs and minimal material waste.
Casting and Die-Casting:
Process: Use of powders in die-casting or compaction processes.
Applications:
Automotive engine parts, structural components, and housings.
Features: The use of atomized powders improves the mechanical properties of cast parts, reducing defects like porosity and improving overall strength.
Powder Coating:
Process: Electrostatic spraying followed by curing.
Applications:
Coatings for automotive parts (bumpers, wheels), appliances, and architectural elements (window frames).