| Potassium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5182 |
| CAS | 7789-23-3 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | KF |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 58.09 g/mol |
| Density | 2.48 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 858° C |
| Boiling Point | 1,502° C |
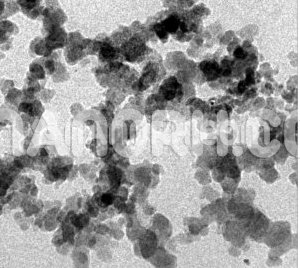
Potassium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Introduction
Potassium fluoride nanoparticles is an inorganic salt consisting of potassium (K) and fluoride (F). Potassium fluoride nanoparticles refer to the fine particulate form of this compound, characterized by its small particle size, high surface area, and unique physical and chemical properties that emerge at the nanoscale.
Applications
Potassium fluoride nanoparticles find applications in several fields, including materials science, catalysis, chemical processing, environmental management, and electronics. Below are some key applications of KF nanoparticles:
Catalysis and Chemical Synthesis
Fluorination Reactions: KF nanoparticles are widely used in fluorination reactions, where they serve as a source of fluoride ions. These reactions are essential for the synthesis of fluorinated organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty polymers.
Catalytic Processes: KF nanoparticles are employed as catalysts or catalyst supports in various organic reactions, including the production of fluorine-containing compounds. Their high surface area enhances the efficiency of these catalytic processes.
Environmental Remediation
Fluoride Removal: Potassium fluoride nanoparticles can be used to remove fluoride ions from water or wastewater. This is particularly important in areas where high fluoride levels pose environmental and health risks.
Pollution Control: KF nanoparticles are also useful in the remediation of toxic metals and contaminants in the environment. Their ability to bind to metal ions allows them to be employed in water purification and air filtration systems.
Electronics and Energy Storage
Electrolytes in Batteries: KF nanoparticles are being investigated for use in lithium-ion or sodium-ion battery electrolytes. Their ability to stabilize the fluoride ion in electrolytes could improve the performance and stability of next-generation batteries.
Supercapacitors: KF nanoparticles may also play a role in the development of supercapacitors by enhancing charge storage capacity and improving the conductivity of electrode materials.