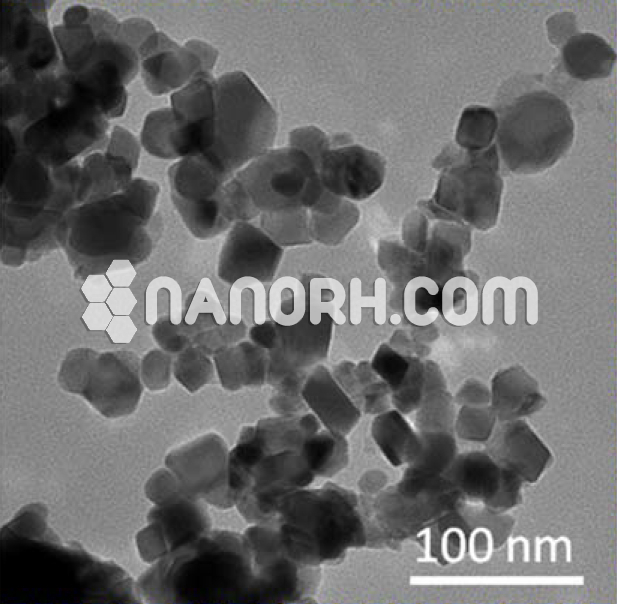
| Gallium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5084 |
| CAS | 7783-51-9 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | GaF3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 126.72 g/mol |
| Density | 4.47 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 800° C |
| Boiling Point | 1,000° C |
Gallium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Applications
Optical Coatings:
Due to their wide bandgap, GaF₃ nanoparticles are used in optical coatings for lenses and mirrors in UV optical systems. They are also used to enhance the transparency of optical devices and as coatings for laser systems due to their ability to withstand high-intensity light.
Laser Technology:
Gallium fluoride nanoparticles are being explored for use in solid-state lasers, particularly in UV laser systems, where their thermal stability and optical properties can enhance performance in devices like laser printers, scanners, and medical lasers.
Fluorescent Sensors:
GaF₃ nanoparticles are often doped with rare earth ions such as Eu³⁺ or Tb³⁺ to produce fluorescent probes for sensing applications. These probes are used in biosensors for detecting bio-molecules, ions, or pollutants. The fluorescence emission from these doped nanoparticles can be tuned to emit light at specific wavelengths, making them suitable for medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
Catalysis and Chemical Applications
Catalytic Reactions:
The high surface area and reactivity of GaF₃ nanoparticles make them excellent candidates for catalytic applications. They can be used as catalysts or catalyst supports in reactions like hydrogenation, oxidation, and dehydrogenation. Their ionic conductivity also contributes to their catalytic efficiency in processes requiring the transfer of ions.
Fluoride Catalysis:
Gallium fluoride nanoparticles are investigated for use in fluoride-catalyzed reactions, where their fluoride ions can facilitate various chemical reactions, such as in organic synthesis or material processing.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Solid-State Electrolytes:
Due to their ionic conductivity, GaF₃ nanoparticles are being explored for use as solid-state electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries and solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Their ability to conduct ions at elevated temperatures makes them suitable for high-temperature energy storage and conversion systems.
Supercapacitors:
GaF₃ nanoparticles are also researched for use in supercapacitors, where their high surface area can improve the charge storage capacity and energy density of these energy storage devices.
Biomedical and Imaging Applications
Bioimaging:
Gallium fluoride nanoparticles, particularly those doped with rare-earth elements, are being explored for bioimaging applications due to their fluorescent properties. These nanoparticles can be used as contrast agents in fluorescence imaging and cell labeling, helping in diagnostic imaging of tissues or cells.