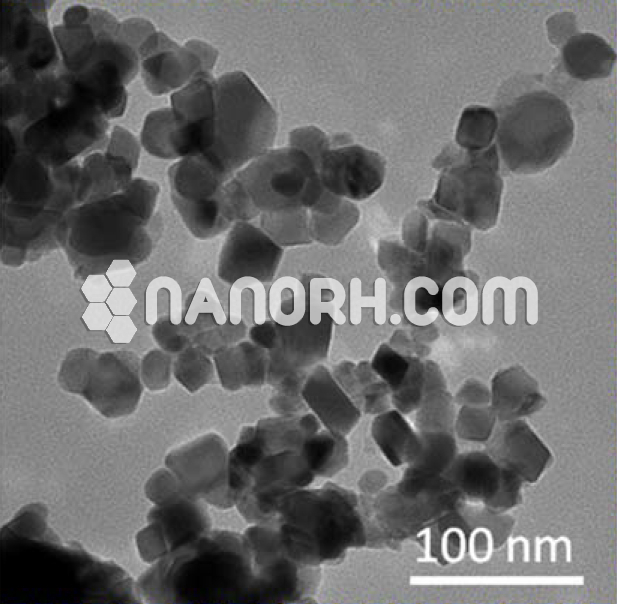
| Bismuth Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5025 |
| CAS | 7787-61-3 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | BiF3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | grey-white |
| Molecular Weight | 265.98 g/mol |
| Density | 5.32 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 649 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Bismuth Fluoride Nanoparticles
Applications
Optical and Photonic Applications:
Optical Coatings and Lenses: Due to their high refractive index and optical transparency, bismuth fluoride nanoparticles are used in optical coatings and lenses for devices requiring high light transmission and focus control. Their use in optical fibers, waveguides, and microlenses is an area of growing interest in photonics.
Luminescent and Light Emitting Devices:
Photoluminescence: Bismuth fluoride nanoparticles can exhibit photoluminescent behavior, making them valuable for use in display technologies, optical sensors, and bioluminescence-based applications. They are particularly useful in applications where UV to visible light emission is required.
Fluorescence Imaging: In biomedical imaging, the nanoparticles’ luminescent properties make them excellent candidates as fluorescent probes for use in in vitro and in vivo imaging. Their biocompatibility and size enable them to be used in sensitive detection and tracking applications.
Catalysis:
Photocatalysis: Bismuth fluoride nanoparticles are photocatalytically active and can be used in processes like water splitting for hydrogen generation or the degradation of pollutants in wastewater. Their enhanced surface area and optical properties make them suitable for environmental cleanup and renewable energy production.
Organic Synthesis: Bismuth fluoride nanoparticles are employed as catalysts in organic synthesis reactions. They offer an environmentally friendly alternative to toxic heavy metals in catalytic processes, providing more sustainable methods for chemical production.
Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery Systems: Due to their low toxicity and biocompatibility, are being investigated for use in drug delivery systems. Their ability to carry and release drugs in a controlled manner makes them potential candidates for targeted drug delivery and therapy.
Medical Imaging: As mentioned earlier, the luminescent properties of make them excellent candidates for use as contrast agents in medical imaging techniques such as fluorescence microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They can enhance the contrast and resolution in imaging systems, helping with the detection of tumors or infections.