| Gadolinium Carbonate Hydrate Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-5082 |
| CAS | 38245-36-2 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | Gd2(CO3)3•xH2O |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | NA |
| Molecular Weight | 494.53 g/mol |
| Density | NA |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
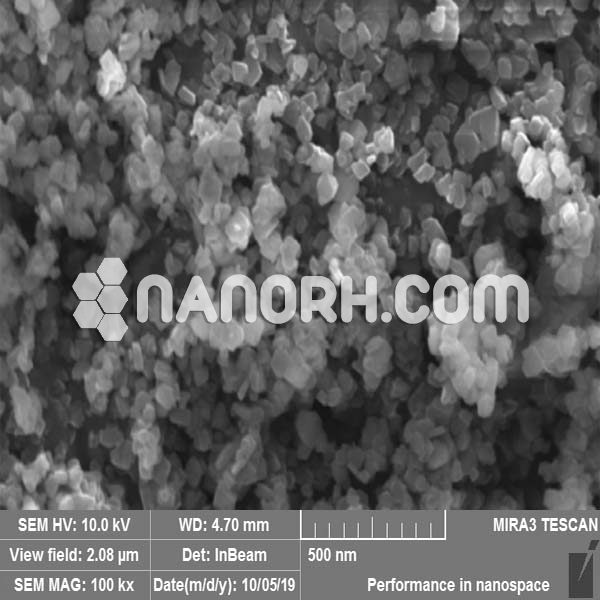
Gadolinium Carbonate Hydrate Nanoparticles
Gadolinium carbonate hydrate nanoparticles are a type of gadolinium-based compound where gadolinium (Gd), a rare-earth element, is chemically bonded with carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻) in a hydrated form. Gadolinium is known for its unique magnetic properties, particularly its use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) due to its paramagnetic behavior, which significantly enhances the contrast in MRI scans. The nanoparticle form of gadolinium carbonate hydrate provides advantages such as increased surface area, biocompatibility, and size-dependent properties, making it highly valuable for a wide range of scientific, medical, and industrial applications.
The hydrated form of gadolinium carbonate is typically synthesized through aqueous reactions involving gadolinium salts and carbonate sources, resulting in nanoparticles that can be used in imaging, catalysis, energy storage, and biomedical applications. The unique combination of gadolinium’s magnetic properties and the high surface area of nanoparticles enhances the effectiveness of these materials in numerous advanced technologies.
Properties
Magnetic Properties:
Gadolinium (Gd) is known for its paramagnetic properties, meaning it has unpaired electrons that align with an external magnetic field, enhancing the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast. Gadolinium carbonate hydrate nanoparticles exhibit strong paramagnetism due to the presence of Gd³⁺ ions, making them useful in MRI contrast agents and other magnetic applications.
Superparamagnetism can also occur in nanoscale materials, making gadolinium carbonate hydrate nanoparticles highly responsive to external magnetic fields, which is important in applications like magnetic targeting and biomedical imaging.
High Surface Area and Reactivity:
At the nanoscale, the high surface area of gadolinium carbonate hydrate nanoparticles significantly increases their reactivity and makes them highly suitable for drug delivery systems, biosensors, and catalytic applications.
The hydration aspect (presence of water molecules) further enhances their ability to interact with biological environments, which is beneficial for bioapplications like drug loading, targeted therapy, and imaging.
Luminescent Properties:
Gadolinium-based nanoparticles can exhibit certain luminescent properties, especially under UV excitation, due to f-electron transitions in the gadolinium ion. This makes them useful for fluorescence-based sensing and biological imaging.