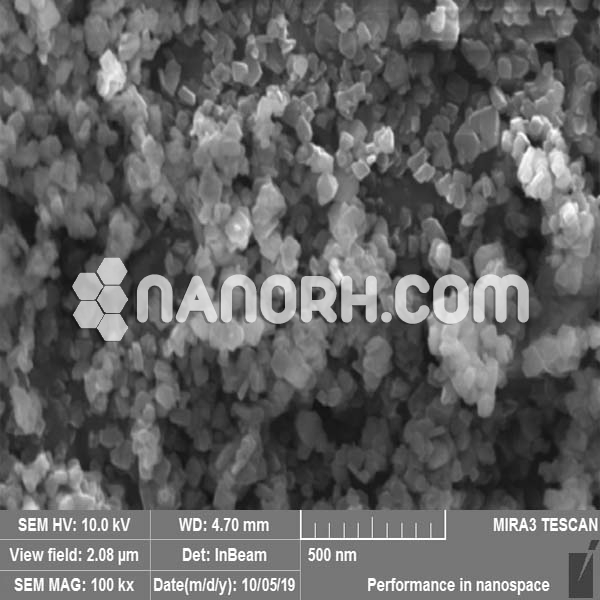
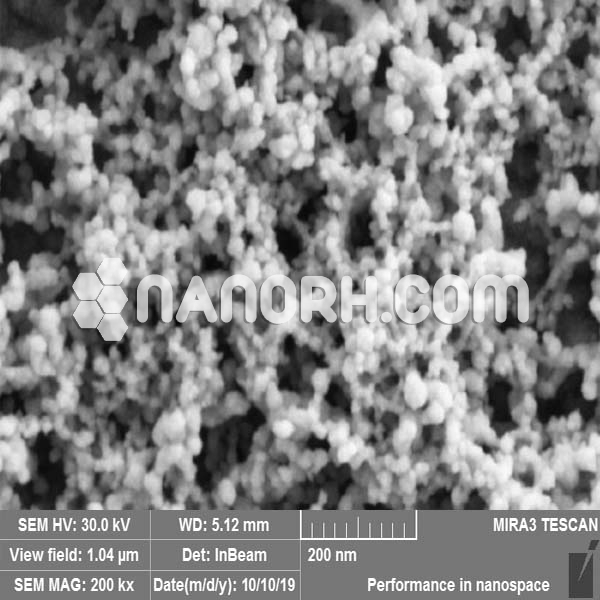
| Indium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5107 |
| CAS No. | 7783-52-0 |
| Formula | InF3 |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | white |
| Molecular Weight | 171.81 g/mol |
| Density | 4.39 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1,172° C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Indium fluoride nanoparticles is a compound consisting of indium (In) and fluorine (F), and it typically exists as a white crystalline solid in its bulk form. When produced as nanoparticles, indium fluoride exhibits significantly enhanced properties compared to its bulk counterpart due to its increased surface area, high reactivity, and quantum effects. These properties make highly useful in a variety of applications across industries, particularly in the fields of electronics, catalysis, optics, and nanomedicine.
Applications
Electronics and Optoelectronics:
Photodetectors: can be utilized in photodetectors that operate in the infrared and visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Due to their ability to absorb light and convert it into electrical signals, they find applications in optical communication systems, night vision devices, and imaging sensors.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): Due to their semiconducting properties and ability to emit light, InF₃ nanoparticles can be incorporated into LEDs and display technologies. These devices benefit from the nanoparticle’s improved performance in terms of efficiency and brightness.
Solar Cells: Indium fluoride nanoparticles have potential in solar cell technology, where their semiconductor properties can enhance the conversion efficiency of photovoltaic devices, especially in thin-film and quantum dot solar cells.
Catalysis:
Heterogeneous Catalysis: Indium fluoride nanoparticles are effective as catalysts in a wide range of chemical reactions. Their high surface area and reactivity make them suitable for processes such as hydrogenation, oxidation, C-H activation, and carbon-carbon coupling reactions. They are also used in the synthesis of organic compounds, where they facilitate faster reaction rates and higher yields.
Environmental Catalysis: Due to their catalytic efficiency, can help degrade harmful organic compounds and pollutants in industrial waste. They are also being explored in the treatment of wastewater and for the removal of heavy metals from contaminated environments.