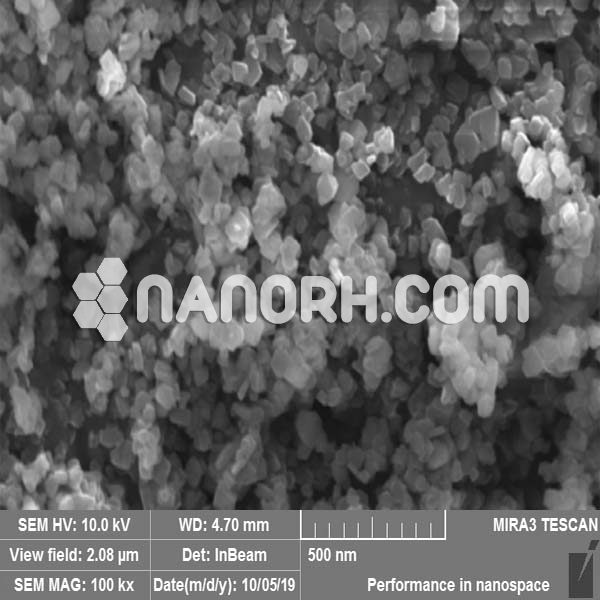
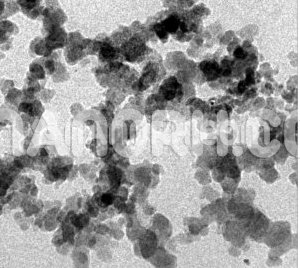
| Indium Chloride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5106 |
| CAS No. | 10025-82-8 |
| Formula | InCl3 |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | white |
| Molecular Weight | 221.177 g/mol |
| Density | 3.46 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 586 °C |
| Boiling Point | 800 °C |
Indium Chloride Nanoparticles
Indium chloride nanoparticles is a chemical compound formed from indium (In) and chlorine (Cl). It typically appears as a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water and other solvents. When synthesized as nanoparticles, indium chloride exhibits enhanced properties compared to its bulk counterpart, such as increased surface area, reactivity, and quantum effects.
Applications
Electronics and Optoelectronics:
Photodetectors: can be used in photodetectors that operate in the infrared or visible spectrum. Their optical properties make them suitable for applications in optical communication, imaging systems, and security devices.
Transistors: The semiconductor properties of InCl₃ nanoparticles make them promising materials for the fabrication of transistors and other microelectronic components. These devices are crucial for nanoelectronics, where small-scale, high-performance devices are required.
Catalysis:
Catalysis in Chemical Reactions: have shown promise in catalytic applications, especially in heterogeneous catalysis. They can be used to accelerate reactions such as hydrogenation, oxidation, and carbon-carbon coupling. Their high surface area and reactivity make them effective catalysts in various industrial processes.
Sensing and Detection:
Gas Sensing: Indium chloride nanoparticles can be used in gas sensors due to their sensitivity to various gases such as ammonia (NH₃), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ). The nanoparticles can detect the presence of these gases based on changes in their electrical or optical properties.
Biosensing: InCl₃ nanoparticles are also being researched for use in biosensors. Functionalizing these nanoparticles to interact with biomolecules can enable highly sensitive detection of biological markers in medical diagnostics, such as DNA, proteins, or pathogens.
Medical Applications:
Drug Delivery: Indium chloride nanoparticles may be used in nanomedicine, particularly in drug delivery systems. Their ability to be functionalized and their high surface area can be leveraged to target specific cells or tissues, improving the efficiency and precision of treatments.