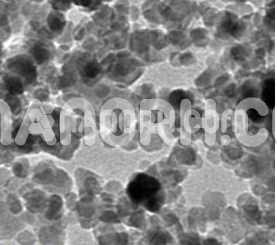
| Indium Iodide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5108 |
| CAS | 13966-94-4 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | InI |
| Molecular Weight | 241.72 g/mol |
| Color | deep red-purple |
| Density | 5.32 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 351 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Iodide Nanoparticles
Applications
Electronics and Optoelectronics
Photodetectors: Indium iodide nanoparticles are promising candidates for photodetectors because they can efficiently absorb light, especially in the UV-visible range, and convert it into an electrical signal. This makes them useful in applications like optical communications, security systems, and imaging devices.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): The semiconducting properties of indium iodide make it suitable for LEDs and laser diodes, particularly for applications that require high-efficiency light-emitting devices. InI nanoparticles can improve the performance and efficiency of displays, solid-state lighting, and photonics devices.
Solar Cells: InI nanoparticles can be used in thin-film solar cells or quantum dot solar cells. Their ability to absorb light and convert it into electrical energy makes them a potential material for enhanced energy conversion efficiency in solar power technologies.
Catalysis
Catalytic Reactions: Indium iodide nanoparticles, with their high surface area and reactivity, can be used as catalysts in various chemical processes such as oxidation, hydrogenation, and C-H activation reactions. These reactions are essential in industries like fine chemicals production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and materials synthesis.
Environmental Catalysis: Indium iodide nanoparticles can also play a role in environmental catalysis, particularly in the degradation of pollutants or the removal of toxic substances such as heavy metals and organic contaminants from wastewater.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors: The high surface area and conductivity of indium iodide nanoparticles make them ideal candidates for use in supercapacitors. Supercapacitors are energy storage devices that can store and release energy quickly, making them suitable for applications in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and grid energy storage.
Batteries: InI nanoparticles are also being researched for use in batteries, particularly in lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries, where their electronic properties and capacity can improve energy storage and enhance battery efficiency.