| Manganese Selenide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5153 |
| CAS | 1313-22-0 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | MnSe |
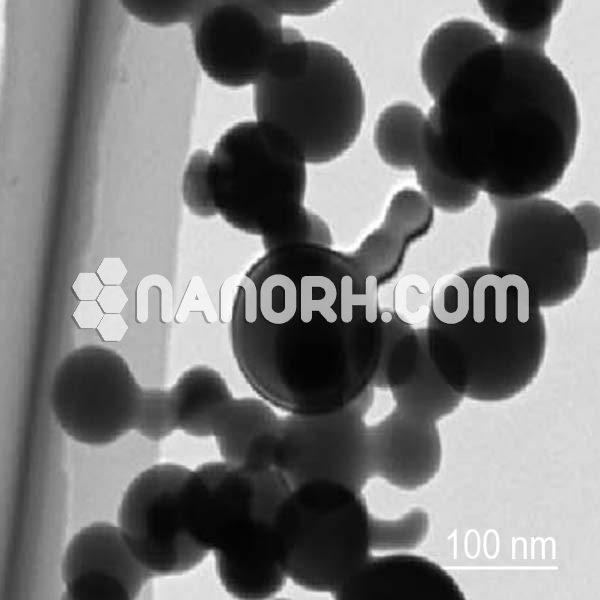
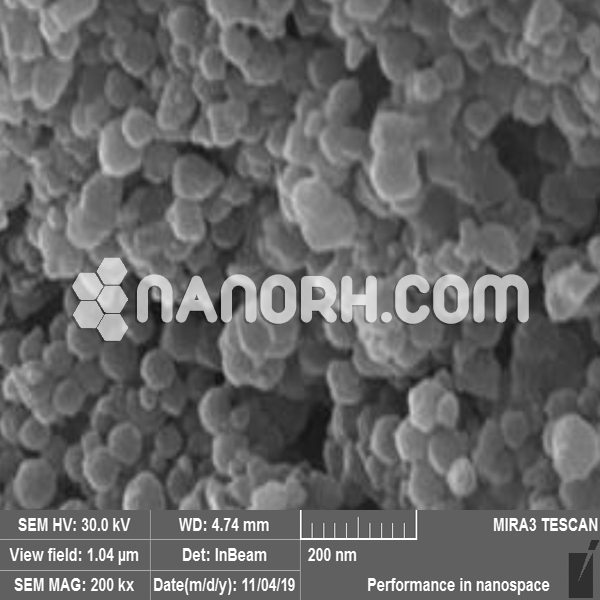
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Color | Grey crystals |
| Molecular Weight | 133.9 g/mol |
| Density | 5.45-5.59 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1460 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Manganese selenide Nanoparticles
Introduction
Manganese selenide (MnSe) is an inorganic compound formed by the combination of manganese and selenium. In nanoparticle form, manganese selenide exhibits unique properties that differ significantly from its bulk counterpart due to its nanoscale size. Manganese selenide nanoparticles (MnSe-NPs) are typically synthesized through chemical vapor deposition (CVD), hydrothermal synthesis, sol-gel methods, or other solution-based techniques, which enable precise control over their size, shape, and surface characteristics.
Applications
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Manganese selenide nanoparticles can be used as electrode materials in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), enhancing their performance by improving the charge/discharge cycles and overall energy capacity. The high surface area of MnSe-NPs allows for more efficient charge storage, making them a promising material for high-performance batteries.
Supercapacitors: Due to their high conductivity and surface area, MnSe nanoparticles can also be used in supercapacitors, which store energy electrostatically. Their use in supercapacitors could lead to devices that are capable of rapid charge and discharge cycles, ideal for energy storage in portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Photovoltaic Devices: Manganese selenide nanoparticles have potential applications in photovoltaic cells for solar energy conversion. Their semiconductor properties, along with the ability to tune their optical absorption, make them suitable for use in next-generation solar energy devices, potentially improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Catalysis:
Hydrogenation Reactions: Manganese selenide nanoparticles can act as effective catalysts in hydrogenation reactions, where they help convert unsaturated compounds into saturated ones by facilitating the addition of hydrogen. This application is important in the chemical industry, including the production of fuels and fine chemicals.
CO₂ Reduction: MnSe-NPs have also been studied for their potential in the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂), a critical process for mitigating climate change. These nanoparticles can be used to convert CO₂ into useful chemicals, such as hydrocarbons, by leveraging their catalytic activity in electrochemical or photocatalytic systems.
Water Splitting: Manganese selenide nanoparticles can act as catalysts in water splitting reactions, where water is decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen. The produced hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel, contributing to sustainable energy solutions.