| Mercury sulfide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5158 |
| CAS | 1344-48-5 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | HgS |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Color | red |
| Molecular Weight | 232.66 g/mol |
| Density | 8.1 g/mL |
| Melting Point | 580°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Mercury sulfide Nanoparticles
Introduction
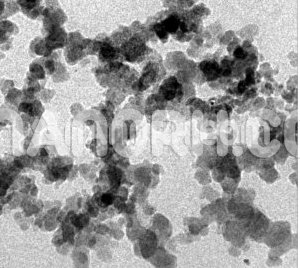
Mercury sulfide nanoparticles are an inorganic compound composed of mercury and sulfur. They typically exist in two polymorphic forms: cinnabar (α-HgS), which is the thermodynamically stable red form, and metacinnabar (β-HgS), a black form of the compound. When reduced to the nanoscale, mercury sulfide exhibits unique properties that differ significantly from those of its bulk counterpart. These properties are largely influenced by the high surface-to-volume ratio, quantum effects, and the ability to control particle size, morphology, and composition during synthesis.
Due to their intriguing electronic, optical, and catalytic properties, HgS nanoparticles have attracted interest in a wide variety of fields, including electronics, energy storage, environmental applications, and biomedical science.
Properties of Mercury Sulfide Nanoparticles
Optical Properties: Mercury sulfide nanoparticles, especially in their nanoparticle form, exhibit unique optical properties such as strong absorption in the visible and ultraviolet regions. The optical bandgap of HgS nanoparticles can be tuned based on their size and shape, making them suitable for use in optoelectronic devices.
Semiconductor Behavior: HgS nanoparticles have semiconductor properties, with a bandgap that varies with particle size. This feature allows them to be used in a wide range of electronic devices, including solar cells and photodetectors.
Toxicity and Environmental Concerns: While mercury sulfide is less toxic compared to other mercury compounds, it is still hazardous due to the potential for mercury release, especially under certain conditions. This necessitates careful handling and disposal when working with HgS nanoparticles in research and industrial settings.
Catalytic Properties: HgS nanoparticles exhibit significant catalytic activity, particularly in reactions such as oxidation, reduction, and dehydrogenation. These properties are valuable in environmental remediation and industrial chemical processes.
Magnetic Properties: In some forms, mercury sulfide nanoparticles show magnetic behavior, which can be exploited in various applications, including in magnetic sensors and other spintronic devices.
High Surface Area: Like most nanoparticles, HgS has a high surface-to-volume ratio, which enhances its reactivity and makes it an excellent material for catalysis, adsorption, and other surface-related applications.