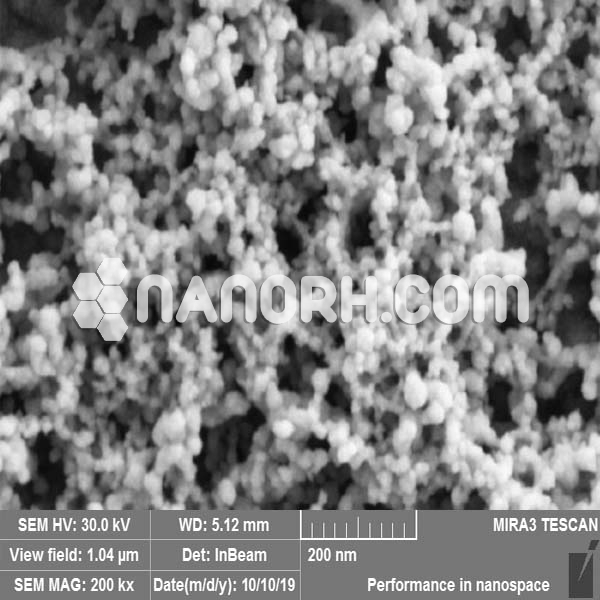
| Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5039 |
| CAS No. | 1306-23-6 |
| Formula | CdS |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Yellow-Orange |
| Molecular Weight | 144.47 g/mol |
| Density | 4.82 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1750 °C |
| Boiling Point | 980 °C |
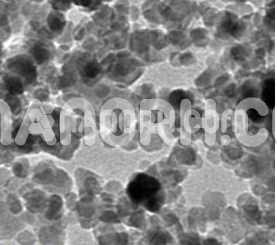
Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles
Cadmium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the recipe CdS. Cadmium sulfide is a yellow strong. It happens in nature with two distinctive precious stone structures as the uncommon minerals greenockite and hawleyite, yet is more predominant as a pollution substituent in the comparably organized zinc metals sphalerite and wurtzite, which are the major monetary wellsprings of cadmium.
Applications of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles
Photovoltaic Devices and Solar Cells:
CdS is widely studied in thin-film solar cells and photovoltaic devices because of its semiconducting properties and light absorption characteristics. The band gap of CdS (~2.4 eV) is well-suited for absorbing visible light, and when used as a buffer layer in solar cells, it enhances the efficiency of solar energy conversion.
Quantum Dots in Optoelectronics:
CdS nanoparticles are often used in quantum dot technologies, where their size-dependent optical properties enable the creation of multicolor light-emitting devices such as LEDs, displays, and lasers. The ability to tune the emission wavelength based on particle size makes them ideal for applications in optical communication and display technologies.
Fluorescent Imaging and Biological Labeling:
CdS nanoparticles are widely used as fluorescent probes in biological imaging and bio-labeling due to their bright fluorescence, chemical stability, and ability to be tuned for specific emission wavelengths. This makes them useful for cellular imaging, tracking biological molecules, and real-time monitoring of biological processes. Their high surface area also allows for functionalization with biomolecules for targeted imaging and detection of specific biomolecules.
Sensing and Biosensing:
CdS nanoparticles are used in chemical sensors and biosensors due to their photoluminescent properties and sensitivity to environmental changes. For example, gas sensors based on CdS NPs can detect gases like hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or carbon dioxide.