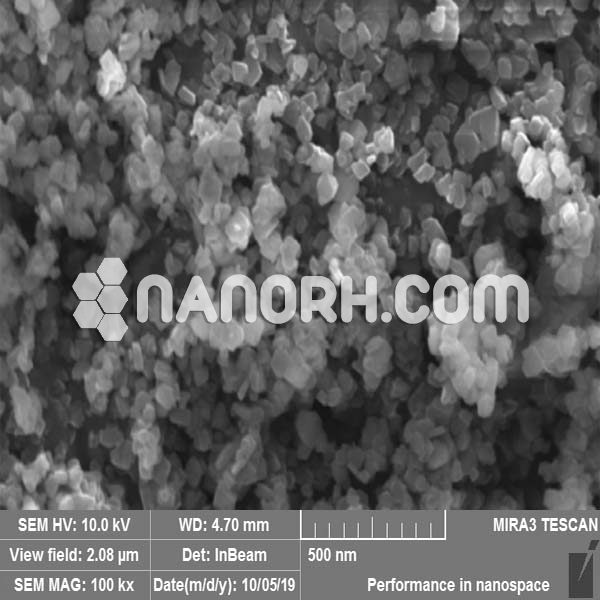
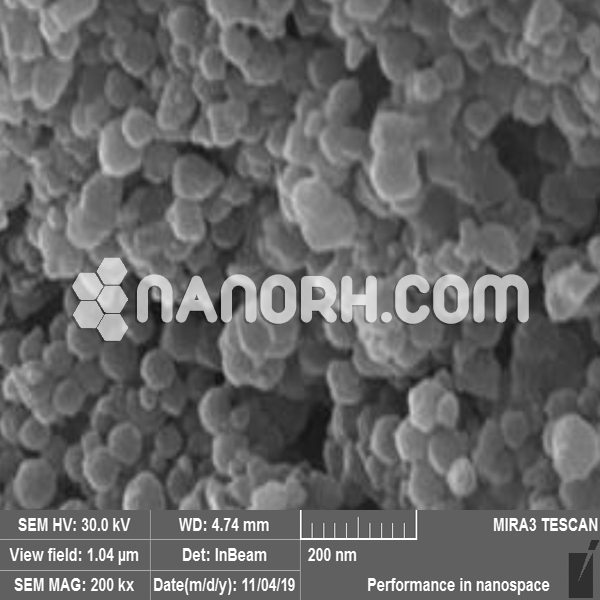
| Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5043 |
| CAS | 7789-75-5 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Formula | CaF2 |
| Molecular Weight | 78.08 g/mol |
| Density | 3.18 g/cm³ |
| Color | Light Cream |
| Melting Point | 1418 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2533°C |
Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Applications:
Optical Materials: Due to their excellent transparency in the UV and infrared regions, CaF₂ nanoparticles are used in the fabrication of optical lenses, windows, and optical fibers. They are widely used in applications that require minimal light absorption and scattering, such as UV optics, infrared optics, and laser technology.
Phosphors and Displays: CaF₂ nanoparticles are also utilized in phosphor materials for display technology, particularly in cathode ray tubes (CRTs) and fluorescent lighting. Their ability to absorb UV light and emit visible light makes them valuable in lighting applications.
Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery and Imaging: The biocompatibility of CaF₂ nanoparticles makes them suitable for drug delivery systems and biomedical imaging. They can be functionalized with specific biomolecules to target particular tissues or cells for controlled drug release or bioimaging.
Catalysis and Chemical Reactions:
Catalysts and Support Materials: The high surface area of CaF₂ nanoparticles makes them excellent candidates for heterogeneous catalysis. They can serve as catalysts or support materials in chemical synthesis and reaction processes, particularly in the production of hydrogen or in photocatalytic applications.
Photocatalysis: CaF₂ nanoparticles have been explored for their ability to act as photocatalysts in environmental applications such as water purification and air cleaning. They can be used to decompose organic pollutants under UV or visible light irradiation.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Batteries and Supercapacitors: Due to their high surface area and electrical properties, CaF₂ nanoparticles can be incorporated into batteries and supercapacitors to enhance energy storage capacity. Their stability at high temperatures also makes them suitable for use in high-temperature energy devices.
Solar Cells: CaF₂ is sometimes explored as a buffer layer or window material in thin-film solar cells due to its low refractive index and transparency to UV and infrared light.