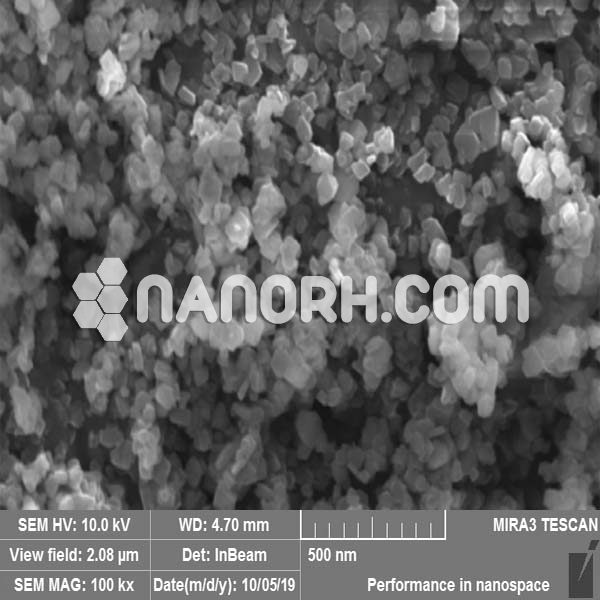
| Iridium Oxide Nanoparticles |
|
| Product Number | NRE-3027 |
| CAS No. | 12030-49-8 |
| Formula | IrO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 224.21/ g/mol |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | Gray |
| Density |
11.66 g/cm³
|
| Melting Point | 1,100 °C |
| Boiling Point | Na |
Iridium Oxide Nanoparticles
Iridium Oxide nanoparticles are a highly valuable class of materials known for their excellent catalytic properties, high corrosion resistance, and stability under extreme conditions. Iridium oxide is an important material in various industrial applications, particularly in catalysis, energy storage, and electrochemical processes.
Applications:
Electrocatalysis and Fuel Cells
Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER): IrO2 are widely used as electrocatalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which is a critical reaction in water splitting, used to generate hydrogen. Due to their high efficiency and stability, iridium oxide nanoparticles are used in alkaline water electrolyzers and proton-exchange membrane electrolyzers (PEM electrolyzers) for hydrogen production.
Fuel Cells: Iridium oxide is used in fuel cells, particularly in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), where it serves as a catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). These fuel cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy and are used in applications ranging from electric vehicles to portable power systems.
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER): Iridium oxide also plays a key role in the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), which is vital for hydrogen production in electrolysis processes.
Energy Storage Systems
Supercapacitors: IrO2 are used in the development of supercapacitors due to their high conductivity and electrochemical stability. These devices store energy electrostatically and are used in applications that require rapid charge and discharge cycles, such as electric vehicles, regenerative braking systems, and mobile electronics.
Batteries: Iridium oxide nanoparticles are used in some advanced batteries, particularly in systems where high performance and long-term stability are required. They can enhance the performance of lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries, as they provide efficient electron transfer and stability during charge/discharge cycles.