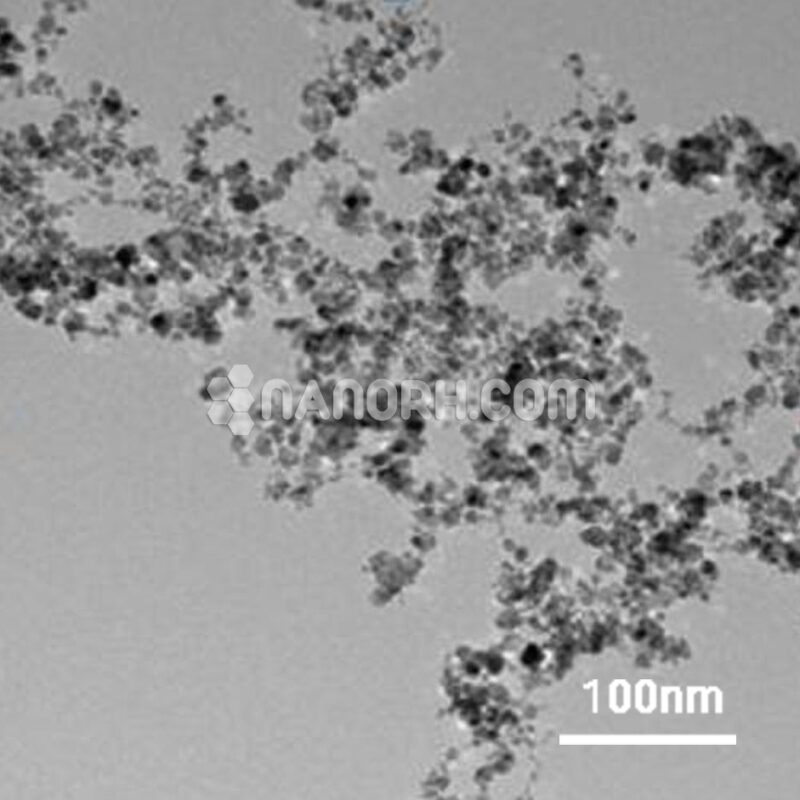
| Platinum Oxide Powder | |
| Product Number | NRE-10044 |
| CAS No. | 1314-15-4 |
| Formula | PtO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 227.07 g/mol |
| APS | <40 µm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | Gray |
| Density | 10.2 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 450 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Platinum Oxide Powder
Introduction:
Platinum oxide powder refers to a family of compounds formed by the combination of platinum (Pt) and oxygen, with the most common being platinum(IV) oxide (PtO₂). This compound is typically a brown to black powder and is widely recognized for its role as an effective oxidizing agent. Platinum oxide is a highly reactive compound that plays a key role in various chemical processes, especially in catalysis and organic synthesis.
Properties of Platinum Oxide Powder:
Physical Properties:
Color: Platinum oxide powder is typically brown or black in color.
Density: Platinum oxide is dense, reflecting the high density of platinum itself.
Solubility: Platinum oxide is insoluble in water but can dissolve in strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid or nitric acid, due to its reactive nature.
Catalytic Activity: It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is capable of promoting a variety of chemical reactions, particularly those involving hydrogenation or oxidation.
Stability: While relatively stable under normal conditions, platinum oxide can decompose at higher temperatures, releasing oxygen gas and leaving behind metallic platinum.
Applications of Platinum Oxide Powder:
In Catalysis:
Hydrogenation Reactions: One of the primary applications of platinum oxide is as a catalyst in hydrogenation reactions. Platinum oxide facilitates the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated organic compounds, converting alkenes to alkanes or reducing carbonyl compounds (such as ketones or aldehydes) to alcohols. This makes it essential in the production of pharmaceuticals, food processing, and the synthesis of fine chemicals.
Oxidation Reactions: Platinum oxide is also used as a catalyst in oxidation reactions to add oxygen to various organic substrates, facilitating the formation of alcohols, aldehydes, and other oxygen-containing compounds.
Petroleum Refining: Platinum oxide is used in the petroleum industry as part of the catalysts for reforming processes, where it helps convert low-value hydrocarbons into higher-value gasoline and other products.