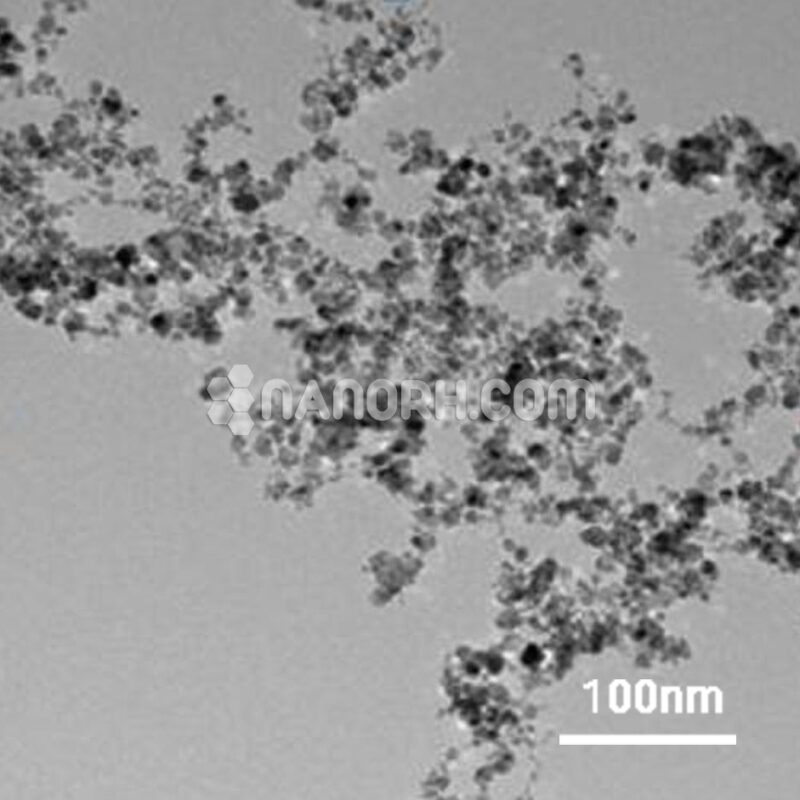
Lithium Oxide Powder
| Lithium Oxide Powder | |
| Product Number | NRE-10032 |
| CAS No. | 12057-24-8 |
| Formula | Li2O |
| Molecular Weight | 29.88 g/mol |
| APS | <40 µm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | White |
| Density | 2.013 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1438 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2600°C |
| Certificate of Analysis | |
| Li | 46.4% |
| O | 53.5% |
| Co | 0.02% |
| Mn | 0.03% |
| Cd | 0.01% |
| La | 0.01% |
Lithium Oxide Powder
Applications:
In Battery Technologies:
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium oxide plays an important role in lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion), where it is a source of lithium for cathodes and anodes. It is used to produce lithium salts such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂) and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄), which are essential components of high-performance rechargeable batteries for consumer electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy storage.
Solid-State Batteries: Lithium oxide is also explored in the development of solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy densities and safer alternatives to traditional liquid electrolyte batteries.
In Ceramics and Glass:
Ceramic Production: Lithium oxide is a key component in ceramics due to its ability to improve the thermal expansion, strength, and durability of ceramic products. It is used in the production of porcelain, stoneware, and fine china to create more thermally stable and durable ceramics.
Glass Manufacturing: In the glass industry, lithium oxide is added to glass formulations to improve thermal shock resistance and optical properties. It is used in the production of specialty optical glass, flat panel displays, and television screens. The addition of lithium oxide to glass helps to reduce the melting temperature and improve productivity.
Frits: Lithium oxide is used in the manufacture of glass frits, which are essential components in ceramic glazes and glass coatings.
In Nuclear Applications:
Nuclear Reactors: Lithium oxide is used in nuclear reactors as a coolant or heat exchanger material, particularly in molten salt reactors. Its high thermal stability and chemical reactivity make it useful in reactor designs that involve high temperatures and corrosive environments.
Fusion Energy: Lithium oxide is also a candidate material for fusion reactors. It is used to produce lithium ceramics that serve as a tritium breeder in fusion reactors, helping to sustain the fusion process by generating the fuel needed for reactions.
In Environmental and Industrial Processes:
CO₂ Capture: Lithium oxide is used in carbon capture technologies where it reacts with carbon dioxide (CO₂) to form lithium carbonate. This reaction is important in environmental control systems aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions in industries like power plants and cement production.
Desiccants and Drying Agents: Due to its high reactivity with water, lithium oxide is used as a drying agent or desiccant in industries that require moisture control, such as in petrochemical processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.