| Potassium Tungstate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5186 |
| CAS No. | 7790-60-5 |
| Formula | K2WO4 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 326.03g/mol |
| Density | 3.12g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 921°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
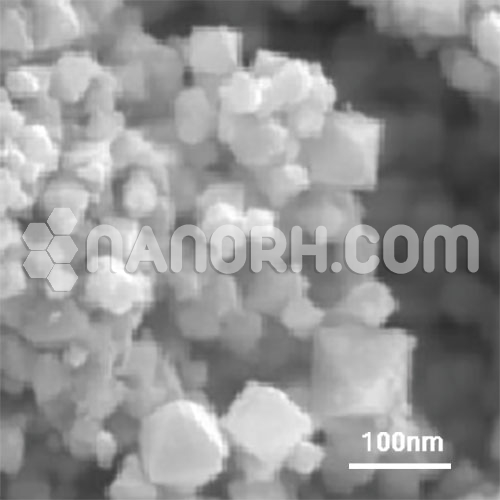
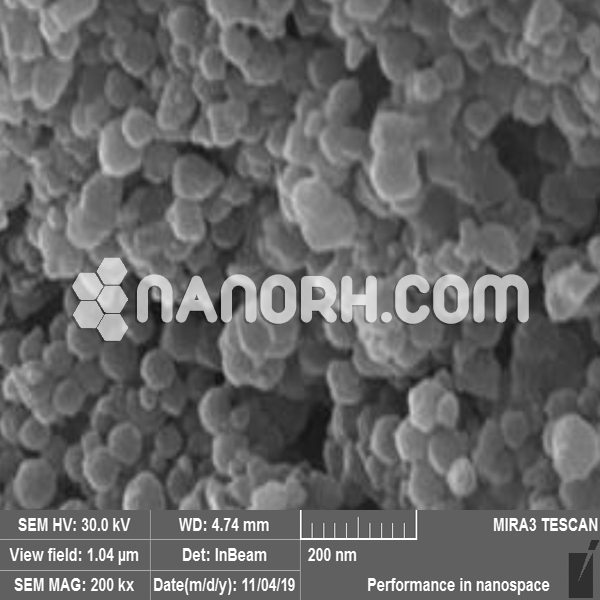
Potassium Tungstate Nanoparticles
Introduction
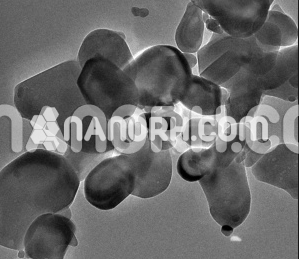
Potassium tungstate nanoparticles is an inorganic compound that contains potassium (K) and tungsten (W) in the form of a tungstate anion (WO₄²⁻). It is typically found as a white or colorless crystalline powder, and when reduced to nanoparticles, potassium tungstate exhibits enhanced properties that differ significantly from its bulk counterpart. These nanoparticles have increased surface area, higher reactivity, and improved material properties, making them suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in fields like catalysis, material science, energy storage, and environmental remediation.
Potassium tungstate nanoparticles can be synthesized using methods like sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These methods allow for precise control over the particle size, morphology, and crystallinity, which can be tailored for specific applications.
Properties
High Surface Area: The nanopowder form of potassium tungstate has a much higher surface area compared to its bulk form, increasing its reactivity and efficiency in various chemical processes.
Catalytic Activity: K2WO4 exhibit excellent catalytic properties, particularly in reactions involving oxidation and reduction processes due to the presence of tungsten, a well-known catalyst in many industrial processes.
Thermal Stability: Tungsten-based compounds, including potassium tungstate, are known for their high thermal stability. These nanoparticles can withstand high temperatures without decomposition, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Optical Properties: can have interesting optical properties, including potential for use in optoelectronic applications like photodetectors and light-emitting devices.
Chemical Reactivity: The increased surface area of enhances their chemical reactivity, making them suitable for various chemical reactions, including catalytic reactions, ion exchange, and material synthesis.
Biocompatibility: While potassium tungstate is generally non-toxic in small quantities, the nanoparticles may offer a more controlled release of ions in biological environments, potentially making them useful in biomedical applications.