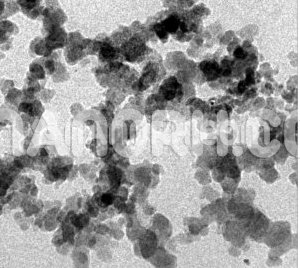
| Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-3007 |
| CAS No. | 1304-76-3 |
| Formula | Bi2O3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | yellow |
| Molecular Weight | 465.96 g/mol |
| Density | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 817°C |
| Boiling Point | 1890°C |
Bismuth Oxide Nanopowder Applications:
Applications:
Catalysis and Environmental Applications:
Photocatalysis for Pollutant Degradation: bismuth oxide nanopowder one of the most promising applications of bismuth oxide nanoparticles is in photocatalysis. Under UV light exposure, Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles can catalyze the degradation of organic pollutants like dyes, pesticides, and industrial waste in water and air. This makes bismuth oxide an attractive material for environmental cleanup, including wastewater treatment and air purification.
Green Energy Applications: Bi₂O₃ has shown potential in solar energy conversion, particularly in photovoltaic devices and solar cells, due to its semiconductor properties. Its photocatalytic properties also make it suitable for solar-driven water splitting to produce hydrogen, a clean energy source.
CO₂ Reduction: Bismuth oxide nanoparticles have been explored for their ability to convert carbon dioxide into useful chemicals using solar energy, contributing to efforts in carbon capture and sustainable energy.
Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery Systems: Due to their biocompatibility, bismuth oxide nanoparticles are explored as carriers for drug delivery. They can encapsulate hydrophobic drugs and provide controlled release in the body. Additionally, the non-toxic nature of bismuth oxide makes it suitable for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy, where it can deliver therapeutic agents to specific tissues with reduced side effects.
Medical Imaging: Bismuth oxide nanoparticles, because of their X-ray attenuation properties, have been investigated for use in medical imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT). Their ability to enhance the contrast in imaging can improve diagnostic accuracy.
Electronics and Optoelectronics:
Photodetectors and Sensors: Bismuth oxide nanoparticles exhibit interesting optical and electrical properties, making them valuable in the development of photodetectors, sensors, and diodes. For instance, they are used in the detection of gases, pollutants, and biomolecules due to their high surface reactivity and semiconducting nature.
Light-emitting Diodes (LEDs): Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles have been integrated into LEDs and laser diodes, especially those targeting the blue and green regions of the light spectrum, thanks to their optical characteristics and ability to interact with light.