Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs)
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs)
| Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-3055 |
| CAS No. | 1317-61-9 |
| Formula | Fe3O4 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Dark Brown |
| Molecular Weight | 231.53 g/mol |
| Density | 5 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1597 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2,623 °C |
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs)
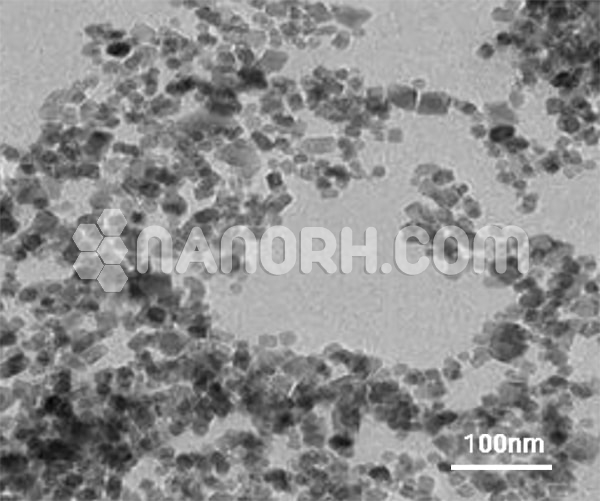
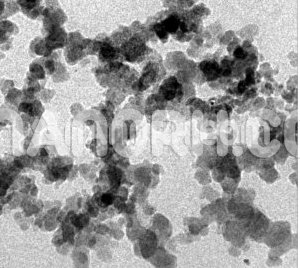
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO; Fe3O4; magnetite) nanoparticles find clinical applications in MRI contrast enhancement. The SPIO nanoparticles produce an enhanced proton relaxation in MRI, especially useful for T2-weighted images. We have used a sonochemical method to synthesize the SPIO nanoparticles having narrow size distribution and highmagnetization. Ferrofluids, or magnetic fluids, from these nanoparticles have shown good MRI image contrast. The SPIO can be incorporated into embolic materials to enable MRI detection and thus find a practical application in embolotherapy. The objective of this study was to develop a novel embolic material capable of MRI contrast enhancement. We prepared spherical SPIO nanoparticles about 15 nm in radius by sonochemistry, and embedded them in chitosan to synthesize a ferrofluid. To make an embolic material, the synthesized ferrofluid was sprayed on the surface of an alkali solution so that the ferrofluid in microsphere form was dispersed in the solution. superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO; Fe3O4; magnetite) nanoparticles and chitosan were developed as a novel MRI-detectable embolic material. Spherical SPIO nanoparticles were synthesized and embedded in polyglucosamine (chitosan) by sonochemical method. The ferrofluid, solution of SPIO-embedded chitosan, was sprayed on the surface of an alkali solution with a nozzle to produce SPIO-chitosan microspheres, from which 100–150 μm microspheres were sifted out.