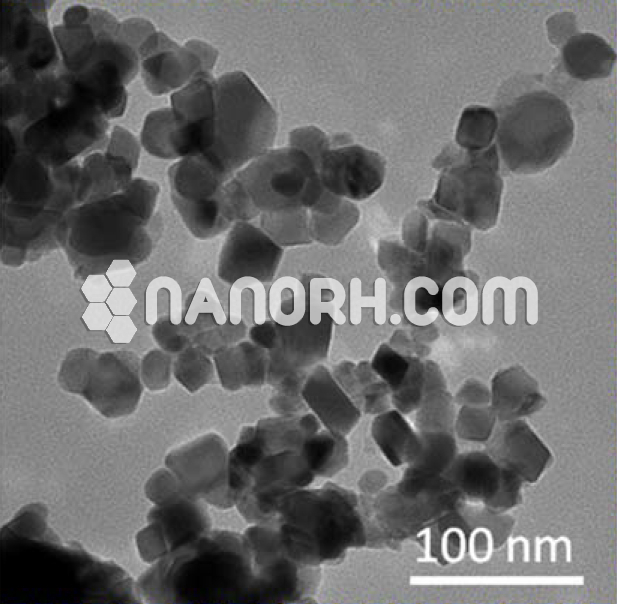
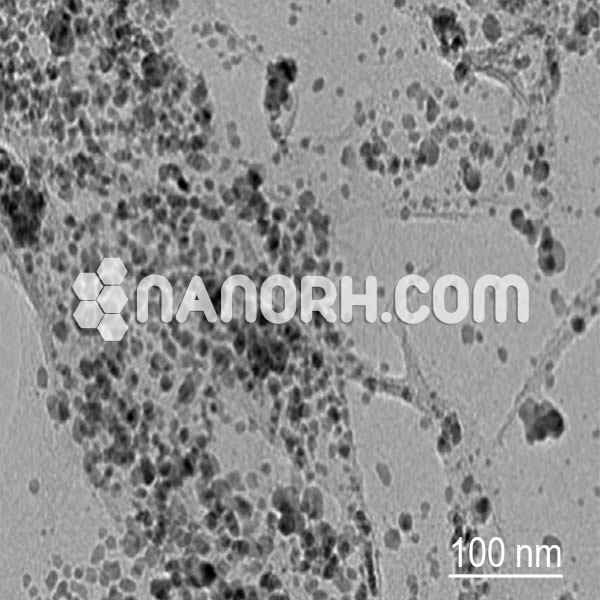
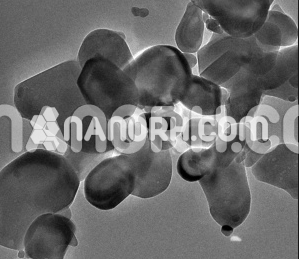
| Rhodium Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-1033 |
| CAS No. | 7440-16-6 |
| Formula | Rh |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 102.91 g/mol |
| Density | 12.41g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1964 °C |
| Boiling Point | 3695 °C |
Rhodium Nanopowder
Rhodium nanopowder has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties and catalytic abilities. Rhodium is a rare and expensive metal, but in nanoparticle form, it can be used more efficiently, making it valuable for various industrial and scientific purposes. Here are some key applications of rhodium nanoparticles:
Catalysis: Rhodium nanoparticles are renowned for their catalytic activity. They are used in various catalytic reactions, such as:
Hydrogenation: Rhodium nanoparticles are used in the hydrogenation of unsaturated organic compounds, including the hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes.
Hydroformylation: Rhodium nanoparticles are employed in the hydroformylation (oxo synthesis) of alkenes to produce aldehydes, a crucial step in the production of various chemicals, including plasticizers and detergents.
Carbonylation: Rhodium nanoparticles can catalyze carbonylation reactions, which are essential in the synthesis of carboxylic acids and esters.
Automotive Catalytic Converters: Rhodium nanoparticles play a vital role in automotive catalytic converters, where they help reduce harmful emissions by catalyzing the conversion of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO) into less harmful compounds.
Electrochemical Sensors: Rhodium nanoparticles can be used in electrochemical sensors for detecting various analytes, including hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and other chemicals. Their high surface area and excellent electrical conductivity make them suitable for this purpose.
Medical Applications: Rhodium nanoparticles have potential applications in medicine, including drug delivery systems and cancer treatment. They can be used to carry drugs to specific targets in the body due to their size and surface properties.
Water Splitting: Rhodium nanoparticles are used in photocatalytic water splitting to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas from water when exposed to sunlight. This technology has implications for renewable energy storage.
Electrocatalysis: Rhodium nanoparticles can serve as electrocatalysts in fuel cells, helping to enhance the efficiency of these devices, which generate electricity by converting chemical energy (e.g., hydrogen and oxygen) into electrical energy.
Plasmonic Properties: Rhodium nanoparticles exhibit unique plasmonic properties, which can be harnessed for applications in sensing, imaging, and nanophotonics.
Hydrogen Storage: Rhodium nanoparticles have been explored for their potential in hydrogen storage materials, which is crucial for the development of hydrogen-powered vehicles and other hydrogen-based energy systems.
Nanoelectronics: Rhodium nanoparticles can be used in nanoelectronic devices and nanoscale circuits due to their small size and excellent electrical properties.