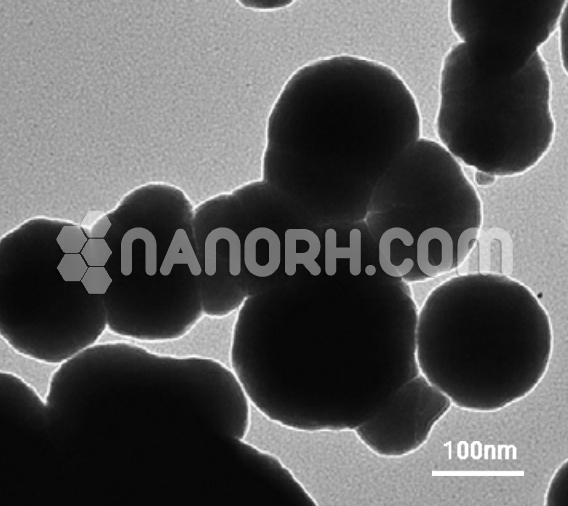
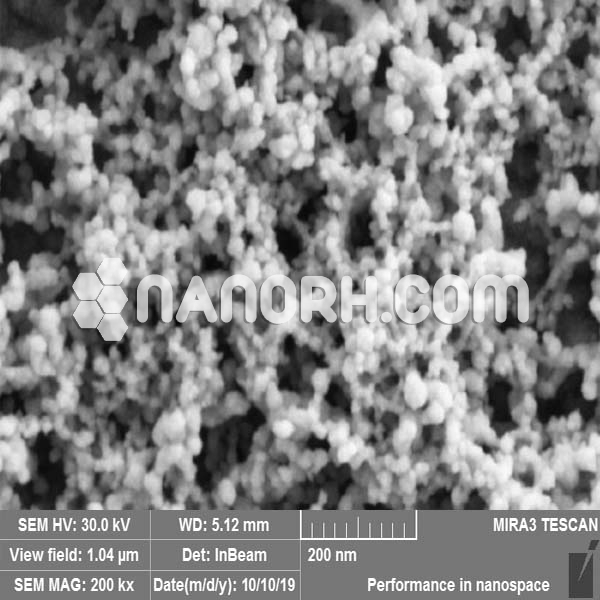
| Iron Carbide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5116 |
| CAS No. | 12127-45-6 |
| Formula | Fe5C2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Black/ Dark Green |
| Density | NA |
| Molecular Weight | 303.2464 g/mol |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Iron Carbide Nanopowder
Introduction
Iron carbide nanopowder also known as cementite, is a chemical compound formed by the combination of iron and carbon. In nanopowder form, iron carbide exhibits unique properties that differ from its bulk counterpart due to the high surface area, small particle size, and enhanced reactivity of nanoparticles.
Applications
Catalysis:
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: One of the primary industrial applications of is as a catalyst in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, which is used to convert syngas (a mixture of CO and H₂) into liquid hydrocarbons. The high surface area and catalytic activity of the nanopowder make it an ideal material for this process, leading to higher reaction rates and better yields of synthetic fuels.
Hydrogenation Reactions: Fe5C2 is employed as a catalyst in hydrogenation reactions, where unsaturated organic compounds (e.g., alkenes) are converted into saturated hydrocarbons. This is a key step in the production of chemicals and fuels in the petrochemical industry.
CO₂ Reduction: Fe5C2 is also being explored for use in the electrochemical reduction of CO₂, which can help mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by converting CO₂ into valuable chemicals, such as carbon monoxide, ethanol, or methane.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Batteries and Supercapacitors: The nanopowder form of iron carbide is being investigated for use in energy storage devices, such as lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. The high surface area and good electrical conductivity of iron carbide nanoparticles help improve the charge/discharge performance and overall energy efficiency of these devices.
Fuel Cells: Iron carbide nanopowder is used as a catalyst in proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, which are devices that convert hydrogen into electricity. The catalytic properties of iron carbide help enhance the efficiency of these fuel cells, making them a promising alternative for clean energy solutions.